About this manual
Objectives
AXIS T8504–E is an outdoor PoE switch. The major benefits of this product is its outdoor capabilities and the capability to extend the maximum reach of the network by an additional 100 meters, to a total of 200 meters, between the switch and the powered devices, while providing up to 2x60 W and 2x30 W to its network-powered PoE devices.
This user manual provides information on how to manage AXIS T8504–E through AXIS IPv4/IPv6, VLAN, RADIUS, TACACS+, web interface, SNMP and SSH.
Intended audience
This user manual is intended for network administrators, supervisors and installation technicians with knowledge about:
Basic concepts and terminology of networking
Network topology including VLAN
Network protocols
User authentication protocols including RADIUS and TACACS+
Related documentation
For additional information, see the following documentation:
Product installation guide
RFC3621 SNMP MIB and private MIB
Creating certificate for T8504–E secured web server
Abbreviations
Abbreviation | Description |
8021.Q | Same as VLAN |
DES | Data Encryption Standard |
DGW | Default Gate Way |
DHCPv4 | Dynamic IPv4 Host Configuration Protocol |
DHCPv6 | Dynamic IPv46 Host Configuration Protocol |
IPv4 | 32–bit long IP address |
IPv6 | 128–bit long IP address |
MD5 | Message digest algorithm |
MDI | Media Dependent Interface |
MIB | Management Information Base |
PoE | Power over Ethernet |
RADIUS | Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service |
SFP | Fiber interface, small form-factor plug |
SHA | Message digest algorithm |
SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
SSH | Secure Shell |
SSL | Secure Sockets Layer |
SysLog | System Log |
TACACS+ | Terminal Access Controller Access-Control |
TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
TLS | Transport Layer Security |
VLAN | Virtual Local Area Network |
General information
Features
A number of features are provided through system network management.
Easy software update during runtime without affecting active PoE ports
Configuration and real-time monitoring using graphical representation of the remote device
System status display
SysLog reporting on PoE events, invalid remote user access, initial DHCPv4/v6 address etc.
SNMP traps reporting on various PoE events such as PoE powered device insertion or removal
Ethernet switch network capabilities
Four weather sealed RJ45 Ethernet ports capable of 10 Mbit, 100 Mbit, 1000 Mbit half-duplex and 1000 Mbit full-duplex Ethernet speed
Single weather sealed SFP Ethernet port
8K internal MAC address lookup engine
VLAN — Access, Trunk and Filtered trunk
Auto MDIX
10KB jumbo frames
PoE capabilities
The following PoE options are available:
Two 4Pair PoE ports which deliver up to 60 W per port
Two IEEE 802.3at PoE ports which deliver up to 30 W per port
PoE enable/disable to enable or disable PoE ports power output. Ethernet data is always enabled.
Remote device reset to reset attached powered device. The device is temporarily powered off and then turned back on.
Supported network protocols
The following network protocols are supported:
IPv4 – 32–bit long IP address (static/DHCPv4)
IPv6 – 128–bit long IP address (static/DHCPv6)
VLAN – Access, Trunk and Filtered trunk
User access and security
Access options
You can access the unit through different interfaces:
Web interface via a web browser – to view the unit PoE status, network status, unit configuration and unit production information
HTTP is a web-based friendly configuration interface.
HTTPS-TLS is a secured web-based friendly configuration interface.
SNMP via an SNMP manager application – to monitor the unit over the network (MIB-II RFC1213) and to monitor or configure the unit PoE capabilities (RFC3621)
SNMPv2c for non-secured SNMP management
SNMPv3 for secured and encrypted management
RFC1213 MIB-II for network statistics
RFC3621 for PoE SNMP MIBs
Private MIB extension for RFC3621 PoE MIB
Various infrastructure and network MIBs such as IP-MIB, TCP-MIB, UDP-MIB etc.
SSH via an SSH client – to view the unit PoE power report, network status, unit configuration and production information; to update software, enable or disable PoE functionality and to ping remote network devices for connectivity tests
Remote user authentication
User access can be managed in the following ways:
Local – Username and password is managed locally by the device
RADIUS – Username and password is authenticated by RADIUS server over the network
TACACS+ – Username and password is authenticated by TACACS+ server over the network
Security protocols
Web HTTP and HTTPS, SNMPv2, SNMPv3 and SSH, used for accessing the unit, offer different levels of security strength. Also RADIUS and TACACS+, used for remote user authentication, offer different security levels.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 use community string for Get/Set/Trap authentication. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 are considered as unsecured protocol since the community string password can easily be intercepted by any network sniffing device.
SNMPv3 resolves SNMPv1/v2 security issues by adding authentication and encryption layer on top of SNMP packets.
Default unit IP, username and password
The unit is shipped with the following factory default usernames and passwords:
Unit default IPv4 address
IP = 192.168.0.254
Mask = 255.255.255.0
Web HTTP/HTTPS and SSH
Username = root
Password = Find the default password on the label on your device
SNMPv2
GET community string = public
SET community string = write
Read community = public
Write community = write
Trap community = public
SNMPv3
Username = admin
Authentication password (MD5) = password
Privacy password (DES) = password
Authentication and encryption mode = MD5+DES
SNMPv3 notification
Username = trap
Authentication password = password
Privacy password = password
Authentication and encryption mode = None
For information about how to recover username and password, see Recover username and password.
Recover username and password
The recovery procedure can only be performed from the local LAN and not over Internet or from another IP network. The user should be able to turn off the unit power when needed. All PoE ports must be disconnected and the unit must have only one single active Ethernet link.
You might need to add a Telnet client service to Windows 7 or Windows 8.
The entire recovery procedure from unit power on until the username and password is applied must take less than 120 seconds.
Disconnect all PoE ports from the unit except for one Ethernet cable. Only one single Ethernet port should be active.
Turn off the firewall or enable UDP port 514. Then run IPv4 capable SysLog Server on your computer.
Turn off the unit. Wait 10 seconds, then turn the unit back on.
A SysLog message appears after approximately 15 seconds. Identify the unit Link-local IPv6 address. A Link-local IPv6 address always starts with FE80.
Open a command window on your computer.
For Windows 7, go to Start and type cmd.
For Windows 8, press the Windows key and the R key, then type cmd.
Type ipconfig to identify the virtual interface index of Link-local IPv6 address. The virtual interface index is indicated by a number after %. Example: fe80::9c39:db8b:62de:7bv4%17
Prepare the SSH connection by typing Telnet [unit Local-link IPv6 address][%virtual interface number] 2525, but don’t press Enter. Example: Telnet fe80::9c39:db8b:62de:7bv4%17 2525
Turn off the unit. Wait 10 seconds, then turn the unit back on.
Wait 30 seconds, then press Enter to start the Telnet session on TCP port 2525.
Type axispasswordrecovery as username and axispasswordrecovery as password. A recovery option to restore the entire unit to complete factory default including unit network configuration is presented.
Press Y to restore the unit. The unit restarts with default IPv4 192.168.0.254, type root as username and use the default password printed on the label on your device.
First-time configuration
When configuring the unit for the first time, follow the steps below:
Configure your PC Ethernet network interface to the following IPv4 parameters:
PC IPv4 address: 192.168.0.40
PC IPv4 mask: 255.255.255.0
Connect your PC Ethernet network interface to any of the unit’s Ethernet ports.
Open a web browser and type 192.168.0.254 in the address field.
Log in with the default username and password. See Default unit IP, username and password.
Configure the unit. It is recommended to change the usernames and passwords to other than the default values.
Unit identification over IP network
To locate the unit over the IP network, the unit sends IPv4 SysLog message #0 in broadcast format 255.255.255.255 upon power-up. Any SysLog server connected over LAN receives this SysLog message. The same SysLog message is also sent to the optional SysLog servers 1 and 2, if they are configured.
The unit sends the message twice. This is to ensure that the SysLog message is received by the SysLog servers, regardless of network configuration. The message is first sent before VLAN configuration is made and later again after VLAN configuration is done.
SysLog message #0 contains all the information which is required to be able to provide access to the unit over the network.
Example: MsgID#000 - System UP. APP:v3.51.06 BOOT:v3.16 RST:Power-On BOOT:0=[APP OK] Host:axis-00055A034B49 MAC:00:05:5a:03:4b:49 VLAN:YES VLAN_MNGR:5 VLAN_UPLINK_PORT:3 VLAN_UPLINK_MODE:TRUNK DHCPv4:No IP1v4:192.168.0.254/24 DHCPv6:No IP1v6:2345::205:5AFF:FE03:4B49/64 IP2v6:FE80::205:5AFF:FE03:4B49/64
Field | Value | Description |
| SysLog message number | |
|
| Unit application software version |
|
| Unit boot version, used for software update |
|
| Reset reason |
|
| |
|
| axis followed by unit MAC address |
|
| Unit MAC address |
|
| VLAN status enabled or disabled |
|
| Ethernet port number used for unit management |
|
| Management port is configured as Access or Trunk |
|
| DHCPv4 Yes or No |
|
| Unit IPv4 address |
|
| DHCPv6 Yes or No |
|
| Unit IPv6 address |
|
| Unit link-local IPv6 address |
Web interface
Web interface menu
Status
Go to Status to view the unit status. The page is updated automatically every few seconds.
The Ethernet network link is always enabled, regardless of PoE configuration (enabled or disabled).
| Parameter | Description |
 | Blue symbol — PoE power is provided Gray symbol — No PoE power |
 | Blue symbol — PoE port is enabled Gray symbol — PoE port is disabled |
 | Blue symbol — Ethernet link is on Gray symbol — No Ethernet link |
 | Blue symbol — SFP module is inserted into the uplink port Gray symbol — Uplink port has no SFP module inserted |
| Network | Reports the Ethernet link speed (10/100/1000 MB) and if the network connection is up or down |
| Status | Reports the PoE port status, if it is enabled, disabled, delivering power, etc. |
| Power usage | Reports the actual power consumption and the maximum power it can deliver |
| PoE reset | Click Reset to turn off the PoE port power and restore the PoE power back on. Note A PoE port which is disabled by SSH or SNMP will be enabled after a PoE reset. |
| Total power usage | Reports the aggregated power consumed by all PoE ports and the percentage of the consumed power relative to the internal power supply power capabilities. |
Basic
Go to Basic to view basic information about the product.
- IP address in use
- Go to IP address in use to view information about IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, masks, default gateways and Domain Name Servers (DNS).
- Product information
- Go to Product information to view general product information such as product name, serial number, software version and PoE firmware version, and SFP module information such as SFP type, vendor, part number and serial number.
- Network configuration
- Go to Network configuration to enable or disable DHCP, configure IPv4, IPv6 and network hostname. Hostname is used by both IPv4 and IPv6 to register the unit name in DHCPv4/v6 server. Note that IPv6 uses the FQDN terminology as hostname.
- Network services IPv4/IPv6
- Go to Network services IPv4/IPv6 to configure DNS and SysLog servers.
- PoE configuration
- Go to PoE configuration to configure PoE port power. Four PoE power schemes offer different power distributions between the four PoE ports. All four options comply with the unit maximum power capacities.
60 W: Deliver power over four pairs inside the Ethernet cable. Each pair delivers up to 30 W.
30 W: Deliver power over two out of four pairs inside the Ethernet cable
15.4 W: Deliver power over two out of four pairs inside the Ethernet cable
– –: No PoE power. Ethernet port is enabled and functional, but PoE is disabled.
Security
Security configuration
Go to Security configuration to configure the unit username and password for remote web or SSH access.
Only ASCII characters 33–90 and 94–122 can be used for the username and password fields.
HTTPS
Go to HTTPS to configure whether HTTP or HTTPS (secured web) should be used. When HTTPS is enabled, TLSv1.2 is used to encrypt web network traffic.
To eliminate web browser warning whenever accessing the unit over HTTPS, add an exception rule to the web browser telling the web browser that the website is legitimate or upload a unit self-signed/CA-signed certificate.
RADIUS/TACACS+
RADIUS/TACACS+ enables remote user authentication when user accesses the unit over web or SSH. Username and password are then authenticated by the RADIUS/TACACS+ server.
The advantages with RADIUS/TACACS+ is that username and password are easy to update, especially if many network devices are to be managed.
The disadvantage with RADIUS/TACACS+ is that the unit is not accessible if both RADIUS/TACACS+ servers are down. It is possible to enable Local login fallback which allows the unit to use its local username and password whenever there is no reply from RADIUS/TACACS+ servers.
| Parameter | Description |
| Enable authentication | Configure if RADIUS/TACACS+ should be enabled or disabled. When RADIUS/TACACS+ is disabled, local username and password are used. |
| Enable local login fallback | When local login fallback is enabled, local username and password are used whenever there is no reply from RADIUS/TACACS+ servers. This can happen when the servers are down or in case of a network problem. |
| Authentication protocol | Select either RADIUS or TACACS+ authentication protocol. |
| Shared secret | The same private key string must be configured on both the unit and the RADIUS/TACACS+ server. |
| Primary server IP address | Configure the primary IPv4, IPv6 or hostname to be used to access the main RADIUS/TACACS+ server. |
| Secondary server IP address | Configure the secondary IPv4, IPv6 or hostname to be used to access the main RADIUS/TACACS+ server. |
| Timout (Sec) | Configure the time for a reply timeout. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Authentication UDP port | Configure the UDP port used by the RADIUS server. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Authentication TCP port | Configure the TCP port used by the TACACS+ server. |
Software version 3.51.06 only supports accessing RADIUS/TACACS+ servers over IPv4, either with an IPv4 address or a hostname to be resolved by DNS server.
Test RADIUS/TACACS+
Go to Test RADIUS/TACACS+ to verify the RADIUS/TACACS+ configuration before activating it.
During testing, the Enable authentication should be disabled.
Configure all RADIUS/TACACS+ parameters, leaving the Enable authentication disabled.
Save the configuration. If not, the parameters will be restored to saved values after each test, erasing any unsaved value.
Type the username and password.
Click Test configuration. A waiting message will appear, followed by either OK or FAIL.
If needed, change and save the configuration and test again.
When the test result is OK, set Enable authentication to enabled. Save the configuration, which activates the RADIUS/TACACS+ configuration.
VLAN configuration
VLAN configuration sanity check is done upon unit power-up and when a VLAN configuration change is requested over the web. The sanity check is to make sure that the unit remains manageable over the network after VLAN configuration is applied. In case the new VLAN configuration may cause the unit to become unmanageable, an error message appears on the webpage for requests over the web. When a problem is detected upon power-up, the unit configuration will be restored to factory default.
| Parameter | Description |
| Enable VLAN | Enable or disable VLAN functionality. |
| Management uplink port | This parameter has no effect on actual VLAN traffic. The management uplink port assists the unit to evaluate if the new VLAN configuration might block the unit from being managed over VLAN from this port. If a possible conflict is detected, an error message appears and the new VLAN configuration is rejected. |
| Management VLAN ID | Configure which VLAN ID to be used when managing the unit whenever VLAN is enabled. |
| Parameter | Description |
| VLAN mode | Set VLAN mode to Access or Trunk for each of the Ethernet ports. Access — VLAN is used only inside the unit to split or limit packet access to specific ports only. Any incoming VLAN tagged packets received by VLAN access port is discarded. VLAN tagging is added to the unit packet for VLAN Access incoming packets. Unit internal VLAN tagging is stripped out for VLAN Access outgoing packets. Trunk — All Ethernet packets are VLAN tagged. Any untagged VLAN packets received by VLAN trunk port is discarded. |
| Access mode VLAN ID | Configure the VLAN ID to be used whenever the port is configured as Access. The unit internal management port acts as access only. It can only be reached from a single management VLAN ID. |
| TRUNK – Filter unknown VLAN | Configure the VLAN Trunk port as filtered or unfiltered. Enabled — Only data flow from some VLAN IDs, specified in the Trunk VLANs list, passes through VLAN Trunk port. All other VLAN tagged traffic is discarded. Disabled — Data flow from all VLAN IDs passes through VLAN Trunk port. |
| TRUNK VLANs | List the VLAN IDs that may pass through VLAN Trunk port whenever TRUNK – Filter unknown VLAN is enabled. |
SNMP configuration
Go to SNMP configuration to configure parameters applicable to SNMPv2c and SNMPv3.
| Parameter | Description |
| Enable SNMPv2c | Enable or disable SNMPv2c support. |
| Read community | Configure the SNMPv2c GET community string. Example: public. |
| Write community | Configure the SNMPv2c SET community string. Example: private. |
| Trap community | Configure the SNMPv2c Trap community string. Example: public. |
| Parameter | Description |
| System contact | Configure the SNMP MIB-II system contact OiD string. Example: John. |
| System name | Configure the SNMP MIB-II system name. Example: My Unit. |
| System location | Configure the SNMP MIB-II system location. Example: University. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Enable notification | Enable or disable the following PoE trap reports:
|
| Notify exceeded power usage (1–99%) | If enabled, user is notified whenever unit total power consumption (xy%) percentage out of unit max power exceeds or drops below specified value. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Enable SNMPv3 | Enable or disable SNMPv3 support. |
| User name | Configure SNMPv3 username string. |
| Authentication password | Configure SNMPv3 password to be used by MD5/SHA. |
| Privacy password | Configure SNMPv3 password to be used by DES/AES. |
| Authentication and encryption mode | Configure the SNMPv3 authentication and encryption mode. None — no authentication or encryption, which means no security. MD5 — MD5 authentication with no encryption. Packet can be changed, by can easily be analyzed by network sniffers. SHA — SHA authentication with no encryption. MD5+DES — MD5 authentication and DES encryption SHA+DES — SHA authentication and DES encryption MD5+AES — MD5 authentication and AES encryption SHA+AES — SHA athentication and AES encryption |
| Parameter | Description |
| User name | Configure SNMPv3 notification username string. |
| Authentication password | Configure SNMPv3 notification password to be used by MD5/SHA. |
| Privacy password | Configure SNMPv3 notification password to be used by DES/AES. |
| Authentication and encryption mode | Configure the SNMPv3 notification authentication and encryption mode. None — no authentication or encryption, which means no security. MD5 — MD5 authentication with no encryption. Packet can be changed, by can easily be analyzed by network sniffers. SHA — SHA authentication with no encryption. MD5+DES — MD5 authentication and DES encryption SHA+DES — SHA authentication and DES encryption MD5+AES — MD5 authentication and AES encryption SHA+AES — SHA athentication and AES encryption |
| Parameter | Description |
| Trap manager #1 | Configure the first IPv4/IPv6/DNS name of remote SNMP manager server receiving unit trap reports such as Cold-Start, etc. |
| Trap manager #2 | Configure the second IPv4/IPv6/DNS name of remote SNMP manager server receiving unit trap reports such as Cold-Start, etc. |
Maintenance
- Reset
- There are four different reset options:
Do a safe restart without losing PoE power resets the internal network manager and the internal Ethernet switch (network will be down for a few seconds), leaving the PoE power unchanged. Powered devices continue normal operations as if no reset is done.
Do a safe restart resets the internal network manager, internal PoE controller and internal Ethernet switch.
Restore the factory values but keep the IP settings resets unit configuration to factory default, leaving IPv4/IPv6 network configuration unchanged. VLAN and RADIUS/TACACS+ is disabled. The option to access the unit over the network as before is maintained.
Restore all factory values restores the unit to full default factory setting. Unit IP is set to 192.168.0.254 and VLAN is disabled.
- Firmware upgrade
- A firmware upgrade upgrades only the internal network manager. PoE firmware is unchanged. The upgrade can take up to 10 minutes. During this time network switching functionality remains uninterrupted, but the unit is unmanageable. PoE functionality remains active, but network traffic may be interrupted for several seconds.
- Product configuration
- Go to Product configuration to download or upload a product configuration file. This functionality can be used to backup unit configuration, modify unit configuration offline or to create a master configuration file to easily configure several units.
SSH serial interface
The SSH interface is designed for various maintenance tasks such as PoE firmware update etc. It is designed to provide an easy and convenient interface for IT managers who are familiar with SSH. To simplify SSH usage, the SSH interface is menu-driven.
SSH is password protected and shares the same username and password as for web access.
SSH supports RADIUS and TACACS+ username and password authentication.
Only one remote user at a time can access the unit over SSH. In case a second remote SSH user tries to access the unit while the first SSH user is still active, a message is shown to the second SSH user, requesting the user to try and reconnect over SSH later.
Non-active SSH sessions (no keystrokes by the remote user) are terminated automatically after three minutes.
Main menu
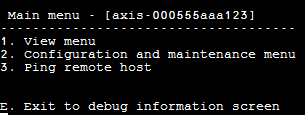
To easily identify the accessed unit, the unit hostname string is shown to the right of the Main menu title. This is especially useful when the user has multiple units.
View menu
View menu provides information on PoE ports status, network parameters and unit information.
Menu item | Description |
1. View PoE ports status | Go to this menu item to get the following information:
|
2. View network parameters | Go to this menu item to get the following information:
|
3. View unit information | Go to this menu item to get a summary of unit production parameters:
|
Configuration and maintenance menu
Go to Configuration and maintenance menu to configure or reset the unit or to update software.
Menu item | Description |
1. Enable/Disable PoE port | Enable or disable a PoE port. Ethernet link remains enabled even when no power is provided. |
2. Download WEB SSL certificate from TFTP server (reset only web server) | Download self-signed or CA signed certificates from a TFTP server, to allow secure web browsing to the unit with security confirmation by the web browser (green lock in the web browser URL area) |
3. Update unit PoE firmware (reset unit) | Update PoE firmware. Update files are downloaded from a TFTP server. PoE functionality is not available during the firmware update (approximately 5–10 minutes). |
4. Restore unit to semi factory default (excluding IP configuration) | Restore the unit configuration to factory default, but leaves the IPv4/IPv6 network configuration unchanged. This maintains the option to access the unit over the network as before. |
5. Restore unit to full factory default | Restore the entire unit to full factory default. |
6. Reset only network manager | Reset only the internal network manager, which is responsible for unit network management interfaces such as the web, SSH, SNMP, etc. Internal Ethernet switch is also reset; the network will be down for a few seconds. Only PoE power is unchanged. Powered devices continue normal operation as if no reset was done. |
7. Reset unit | Reset the entire unit including the internal network manager, PoE controller and internal Ethernet switch. |
8. Enable/Disable auto ping default gateway to ensure network connectivity | Enable or disable auto ping to default gateway. When enabled, the unit verifies proper network connectivity by pinging default gateway every 12 seconds (IPv4 DGW or IPv6 DGW). After 10 consecutive ping failures, network management module resets itself without affecting PoE ports. |
Ping remote host
Go to Ping remote host to test network connectivity issues.
SNMP monitoring and configuration
Multiple units can be monitored and managed by using third-party standard network management tools such as HP Openview, IBM Tivoli, SNMPc etc.
Enable SNMP
The network manager interface supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2 and SNMPv3. The unit accepts and replies to SNMPv1 packets, but since SNMPv1 is obsolete, SNMP traps and notifications are sent in SNMPv2, SNMPv3 or both.
Due to security reasons, the unit is shipped with SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 disabled. Prior to enabling SNMP, it is highly recommended to modify SNMP community strings before enabling it.
To enable SNMP:
Go to Security > SNMMP configuration and enable SNMPv2 or SNMPv3.
Make sure that SNMPv2 community strings match your SNMP manager configuration.
Make sure SNMPv3 username, authentication password, privacy password and encryption methods match your SNMP manager configuration.
To enable traps:
Go to Remote IPv4/IPv6 SNMP trap managers and configure the remote manager IP address.
Make sure SNMPv3 notification username, authentication password, privacy password and encryption methods match your SNMP trap manager configuration.
Go to PoE MIB and enable PoE notifications to get notifications about changes in PoE port status, unit power consumption exceeds or falls below a certain level etc.
SNMP MIBs
Several MIBs are supported by the SNMP manager.
- Network MIBs
- Various network MIBs, such as RFC1213 MIB-II, can be used for providing network statistics. Note that these MIBs are not intended to be used for network configuration over SNMP.
- RFC3621
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) MIB which provides various PoE capabilities. See RFC3621 PoE MIB.
- Private MIB
- Enhances PoE functionality beyond RFC3621 PoE MIB. See Private MIB.
RFC3621 PoE MIB
RFC3621 PoE MIB is located under the 1.3.6.1.2.1.105 SNMP MIB tree. The MIB is divided into three sections.
- Port parameters
- The first section handles PoE ports and provides functionality such as enable and disable ports, read port status, class, etc. Each OiD is accessed as a two-dimensional array table.
- Main PSE parameters
- The second section handles the power source that provides power to a group of PoE ports. It enables reading the total power consumption, power supply status, etc.
- PoE traps
- The third section enables and disables PoE traps to be sent to remote SNMP managers.
Private MIB
The following SNMP OiDs are supported by the SNMP private MIB:
OiD name | Type (R/W) | Description |
poePortConsumptionPower | R | PoE port power consumption [Watt] |
poePortMaxPower | R | PoE port maximum available power [Watt] |
poePortType | R | PoE port type — two pair, 30 [Watt], four pair, 60 [Watt] |
mainVoltage | R | Unit power supply voltage [Volt] |
SysLog Message
The unit sends various event reports to an external IPv4/IPv6 host running a SysLog daemon application. The IPv4/IPv6 host logs the events for future use. Configure SysLog server IP address by browsing to the unit configuration web page if SysLog events are to be sent.
There are three categories of log events:
- Broadcast IPv4 SysLog events
- These log events are to be intercepted by any SysLog server on the LAN regardless of unit SysLog configuration. This facilitates locating of unit IP on the network and reporting of major events such as unit recovery from power failure, etc.
- RFC3621 PoE traps
- RFC3621 PoE traps are also sent as SysLog messages, which simplifies the readability of such events for the remote user.
- Proprietary SysLog events
- These log events include potential failures or potential security breaches as when a remote user tries to access with incorrect username over web/SSH, etc.
SysLog message types
Message ID | Description | Information provided | Comments |
0 | System UP is sent when power is provided to the unit or the internal network manager resets itself. |
| Message is sent in broadcast format 255.255.255.255 to any SysLog server connected over LAN and to SysLog server 1 and 2. |
1 | PoE port status changed is sent when PoE port status is changed, such as when a device is inserted or removed. | New PoE state as defined in RFC3621 (searching, delivering power, fault, etc.) | RFC3621 SNMP PoE MIB, trap equivalent SysLog report |
2 | PoE power usage exceeds xy% out of power supply maximum power is sent when the PoE power usage exceeds the set value. | Power usage in percent out of power supply maximum power | RFC3621 SNMP PoE MIB, trap equivalent SysLog report |
3 | PoE power usage is less than xy% out of power suply maximum power is sent when the PoE power usage goes below the set value. | Power usage in percent out of power supply maximum power | RFC3621 SNMP PoE MIB, trap equivalent SysLog report |
6 | Default configuration is sent when unit is restored to default configuration | SysLog server IP is unchanged when the unit is restored to default configuration. | |
7 | Unit configuration changed is sent when the unit configuration is changed. | ||
9 | PoE controller reset is sent when PoE controller reset occurs. | ||
10 | PoE controller has no firmware is sent when PoE controller firmware is erased or is corrupted. | ||
11 | Invalid SSH is sent when a remote user tries to access the unit by SSH with incorrect username or password. | Remote user IPv4/IPv6 address | |
12 | DHCPv4 is sent only the first time DHCPv4 address is obtained either by switching from static to DHCPv4 or on power-up. |
| Message is sent in broadcast format 255.255.255.255 to any SysLog server connected over LAN and to SysLog server 1 and 2. |
13 | DHCPv6 is sent only the first time DHCPv6 address is obtained either by switching from static to DHCPv6 or on power-up. |
| Message is sent in broadcast format 255.255.255.255 to any SysLog server connected over LAN and to SysLog server 1 and 2. |
14 | Invalid VLAN configuration is sent when the unit upon power-up detects that current VLAN configurations prevent the unit from being managed over the network. This is possibly due to a faulty new configuration file being uploaded to the unit. The unit restores itself to semi factory default, turns off VLAN and restores most of its configuration parameters to factory default, leaving the unit’s network IP parameters unchanged. Then the unit restarts. | Message is sent in broadcast format 255.255.255.255 to any SysLog server connected over LAN and to SysLog server 1 and 2. |
Troubleshooting
The following troubleshooting table guides you through the most common problems. If you cannot find the information you are looking for, contact your local dealer for further assistance.
Problem | Corrective steps |
Pinging the unit IP address fails. |
|
Unit can be pinged from a local host, but when trying to use the unit’s ping utility there is no response. |
|
Software cannot be updated via TFTP. |
|
Log on to the unit by SSH works, but SSH session terminates after a while. | SSH session terminates after three minutes if no key is pressed and no activity takes place. |
No SNMP trap events are received. |
|
SysLog server IP is properly set, but log messages are not received. | Turn off the host firewall or allow UDP port 514 to pass through it. |
Logging in to the unit does not work since RADIUS/TACACS+ was enabled. |
|
PoE SNMP traps are not sent. |
|
Support
Should you require any technical assistance, please contact your Axis reseller. If your questions cannot be answered immediately, your reseller will forward your queries through the appropriate channels to ensure a rapid response. If you are connected to the Internet, you can:
visit axiscompanion.com/manuals for a complete set of product specific user manuals and system installation guides
download user documentation and software updates
find answers to resolved problems in the FAQ database, search by product, category, or phrase
report problems to Axis support staff by logging in to your private support area
chat with Axis support staff
visit Axis Support at axis.com/support
Should you require any technical assistance, please contact appropriate channels according to your AVHS license agreement to ensure a rapid response.
Should you require any technical assistance, please contact ADP Helpdesk to ensure a rapid response.
Learn more!
Visit Axis learning center axis.com/learning for useful trainings, webinars, tutorials and guides.