About this manual
This user manual describes several products. This means you may find instructions that aren’t applicable to your product.
Solution overview
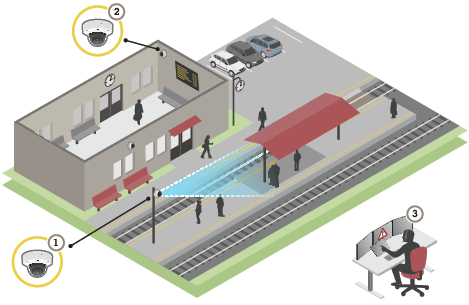
- AXIS P3227-LVE or AXIS P3228-LVE
- AXIS P3227-LV or AXIS P3228-LV
- Surveillance center
This is an example of how the products can be installed and used.
Get started
Find the device on the network
To find Axis devices on the network and assign them IP addresses in Windows®, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager. Both applications are free and can be downloaded from axis.com/support.
For more information about how to find and assign IP addresses, go to How to assign an IP address and access your device.
Browser support
You can use the device with the following browsers:
ChromeTM | EdgeTM | Firefox® | Safari® | |
Windows® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
macOS® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
Linux® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
Other operating systems | * | * | * | * |
✓: Recommended
*: Supported with limitations
Open the device's web interface
Open a browser and type the IP address or host name of the Axis device.
If you do not know the IP address, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager to find the device on the network.
Type the username and password. If you access the device for the first time, you must create an administrator account. See Create an administrator account.
For descriptions of all the controls and options in the device’s web interface, see The web interface.
Create an administrator account
The first time you log in to your device, you must create an administrator account.
Enter a username.
Enter a password. See Secure passwords.
Re-enter the password.
Accept the license agreement.
Click Add account.
The device has no default account. If you lose the password for your administrator account, you must reset the device. See Reset to factory default settings.
Secure passwords
Use HTTPS (which is enabled by default) to set your password or other sensitive configurations over the network. HTTPS enables secure and encrypted network connections, thereby protecting sensitive data, such as passwords.
The device password is the primary protection for your data and services. Axis devices do not impose a password policy as they may be used in various types of installations.
To protect your data we strongly recommend that you:
Use a password with at least 8 characters, preferably created by a password generator.
Don’t expose the password.
Change the password at a recurring interval, at least once a year.
Web interface overview
This video gives you an overview of the device’s web interface.
Installation
Preview mode
Preview mode is ideal for installers when fine tuning the camera view during the installation. No login is required to access the camera view in preview mode. It is available only in factory defaulted state for a limited time from powering up the device.
Configure your device
Image quality
Select exposure mode
To improve image quality for specific surveillance scenes, use exposure modes. Exposure modes lets you control aperture, shutter speed, and gain. Go to Video > Image > Exposure and select between the following exposure modes:
For most use cases, select Automatic exposure.
For environments with certain artificial lighting, for example fluorescent lighting, select Flicker-free.
Select the same frequency as the power line frequency.
For environments with certain artificial light and bright light, for example outdoors with fluorescent lighting at night and sun during daytime, select Flicker-reduced.
Select the same frequency as the power line frequency.
To lock the current exposure settings, select Hold current.
Handle scenes with strong backlight
Dynamic range is the difference in light levels in an image. In some cases the difference between the darkest and the brightest areas can be significant. The result is often an image where either the dark or the bright areas are visible. Wide dynamic range (WDR) makes both dark and bright areas of the image visible.


- WDR can cause artifacts in the image.
- WDR may not be available for all capture modes.
Go to Video > Image > Wide dynamic range.
Turn on WDR.
Use the Local contrast slider to adjust the amount of WDR.
If you still have problems, go to Exposure and adjust the Exposure zone to cover the area of interest.
Find out more about WDR and how to use it at axis.com/web-articles/wdr.
View and record video
This section includes instructions about configuring your device. To learn more about how streaming and storage works, go to Streaming and storage.
Reduce bandwidth and storage
Reducing the bandwidth can lead to loss of detail in the image.
Go to Video > Stream.
Click in the live view.
Select Video format AV1 if your device supports it. Otherwise select H.264.
Go to Video > Stream > General and increase Compression.
Go to Video > Stream > Zipstream and do one or more of the following:
Select the Zipstream Strength that you want to use.
Turn on Optimize for storage. This can only be used if the video management software supports B-frames.
Turn on Dynamic FPS.
Turn on Dynamic GOP and set a high Upper limit GOP length value.
Set up network storage
- To store recordings on the network, you need to set up your network storage.
Go to System > Storage.
Click Add network storage under Network storage.
Type the IP address of the host server.
Type the name of the shared location on the host server under Network share.
Type the username and password.
Select the SMB version or leave it on Auto.
Select Add share without testing if you experience temporary connection issues, or if the share is not yet configured.
Click Add.
Record and watch video
- Record video directly from the camera
Go to Video > Stream.
To start a recording, click .
If you haven’t set up any storage, click and . For instructions on how to set up network storage, see Set up network storage
To stop recording, click again.
- Watch video
Go to Recordings.
Click for your recording in the list.
Set up rules for events
You can create rules to make your device perform an action when certain events occur. A rule consists of conditions and actions. The conditions can be used to trigger the actions. For example, the device can start a recording or send an email when it detects motion, or show an overlay text while the device is recording.
To learn more, see Get started with rules for events.
Show a text overlay in the video stream when the device detects an object
This example explains how to display the text “Motion detected” when the device detects an object.
Start the application if it is not already running.
Make sure you have set up the application according to your needs.
- Add the overlay text:
Go to Video > Overlays.
Under Overlays, select Text and click .
Enter
#Din the text field.Choose text size and appearance.
To position the text overlay, click and select an option.
- Create a rule:
Go to System > Events and add a rule.
Type a name for the rule.
In the list of actions, under Overlay text, select Use overlay text.
Select a video channel.
In Text, type “Motion detected”.
Set the duration.
Click Save.
The web interface
Support for the features and settings described in this section varies between devices. This icon indicates that the feature or setting is only available in some devices.
Show or hide the main menu. Access the release notes. Access the product help. Change the language. Set light theme or dark theme. The user menu contains:
The context menu contains:
|
Status
Security
Shows what kind of access to the device that is active, what encryption protocols are in use, and if unsigned apps are allowed. Recommendations to the settings are based on the AXIS OS Hardening Guide.
Hardening guide: Link to AXIS OS Hardening guide where you can learn more about cybersecurity on Axis devices and best practices. |
Time sync status
Shows NTP synchronization information, including if the device is in sync with an NTP server and the time remaining until the next sync.
NTP settings: View and update the NTP settings. Takes you to the Time and location page where you can change the NTP settings. |
Ongoing recordings
Shows ongoing recordings and their designated storage space.
Recordings: View ongoing and filtered recordings and their source. For more information, see Recordings Shows the storage space where the recording is saved. |
Device info
Shows information about the device, including AXIS OS version and serial number.
Upgrade AXIS OS: Upgrade the software on your device. Takes you to the Maintenance page where you can do the upgrade. |
Connected clients
Shows the number of connections and connected clients.
View details: View and update the list of connected clients. The list shows IP address, protocol, port, state, and PID/process of each connection. |
Video
Click to play the live video stream. Click to freeze the live video stream. Click to take a snapshot of the live video stream. The file is saved in the ‘Downloads’ folder on your computer. The image file name is [snapshot_YYYY_MM_DD_HH_MM_SS.jpg]. The size of the snapshot depends on the compression that the specific web-browser engine where the snapshot is received applies, therefore, the snapshot size may vary from the actual compression setting that is configured in the device. Click to show I/O output ports. Use the switch to open or close the circuit of a port, for example, to test external devices. Click to manually turn on or turn off the IR illumination. Click to manually turn on or turn off the white light. Click to access onscreen controls. Enable groups of onscreen controls to make the settings in each group available when users right-click the live stream in the video management software.
Starts the washer. When the sequence starts, the camera moves to the configured position to receive the wash spray. When the whole wash sequence is completed, the camera returns to its previous position. This icon is only visible when the washer is connected and configured. Starts the wiper. Click and select a preset position to go to that preset position in the live view. Or, click Setup to go to the preset position page. Adds or removes a focus recall area. When you add a focus recall area, the camera saves the focus settings at that specific pan/tilt range. When you have set a focus recall area and the camera enters that area in the live view, the camera recalls the previously saved focus. It’s enough to cover half of the area for the camera to recall the focus. Click to select a guard tour, then click Start to play the guard tour. Or, click Setup to go to the guard tours page. Click to manually turn on the heater for a selected period of time. Click to start a continuous recording of the live video stream. Click again to stop the recording. If a recording is ongoing, it will resume automatically after a reboot. Click to show the storage that is configured for the device. To configure the storage, you need to be logged in as an administrator. Click to access autotracking settings. More settings are available if you click the icon from Analytics > Autotracking. Click to access more settings:
Click to show the live view at full resolution. If the full resolution is larger than your screen size, use the smaller image to navigate in the image. Click to show the live video stream in expanded full screen. Click again to exit the expanded full screen mode. Click to show the live video stream in full screen. Press Esc to exit full screen mode. |
Installation
Capture mode: A capture mode is a preset configuration that defines how the camera captures images. When you change the capture mode, it can affect many other settings, such as view areas and privacy masks. Mounting position: The orientation of the image can change depending on how you mount the camera. Power line frequency: To minimize image flicker, select the frequency your region uses. The American regions usually use 60 Hz. The rest of the world mostly uses 50 Hz. If you're not sure of your region's power line frequency, check with the local authorities. |
Rotate: Select the preferred image orientation. |
Zoom: Use the slider to adjust the zoom level. Autofocus after zooming: Turn on to enable autofocus after zooming. Focus: Use the slider to manually set the focus. Autofocus: Click to make the camera focus on the selected area. If you don’t select an autofocus area, the camera focuses on the entire scene. Autofocus area: Click to show the autofocus area. This area should include the area of interest. Reset focus: Click to make the focus return to its original position. Note In cold environments, it can take several minutes for the zoom and focus to become available. |
Image
Appearance
Scene profile: Select a scene profile that suits your surveillance scenario. A scene profile optimizes image settings, including color level, brightness, sharpness, contrast, and local contrast, for a specific environment or purpose.
Saturation: Use the slider to adjust the color intensity. You can, for example, get a grayscale image.  Contrast: Use the slider to adjust the difference between light and dark.  Brightness: Use the slider to adjust the light intensity. This can make objects easier to see. Brightness is applied after image capture, and doesn’t affect the information in the image. To get more details from a dark area, it’s usually better to increase gain or exposure time.  Sharpness: Use the slider to make objects in the image appear sharper by adjusting the edge contrast. If you increase the sharpness, it may increase the bitrate and the amount of storage space needed as well.  |
Wide dynamic range
WDR: Turn on to make both bright and dark areas of the image visible. Local contrast: Use the slider to adjust the contrast of the image. A higher value makes the contrast higher between dark and light areas. Tone mapping: Use the slider to adjust the amount of tone mapping that is applied to the image. If the value is set to zero, only the standard gamma correction is applied, while a higher value increases the visibility of the darkest and brightest parts in the image. |
White balance
When the camera detects the color temperature of the incoming light, it can adjust the image to make the colors look more natural. If this is not sufficient, you can select a suitable light source from the list.
The automatic white balance setting reduces the risk of color flicker by adapting to changes gradually. If the lighting changes, or when the camera is first started, it can take up to 30 seconds to adapt to the new light source. If there is more than one type of light source in a scene, that is, they differ in color temperature, the dominating light source acts as a reference for the automatic white balance algorithm. This behavior can be overridden by choosing a fixed white balance setting that matches the light source you want to use as a reference.
Light environment:
|
Day-night mode
IR-cut filter:
IR pass filter: Turn on to block visible light and only allow near infrared light to pass through. This toggle button is only available when the IR-cut filter is set to Off. Threshold: Use the slider to adjust the light threshold where the camera changes from day mode to night mode.
IR light If your device doesn’t have built-in illumination, these controls are only available when you connect a supported Axis illuminator. Allow illumination: Turn on to let the camera use the built-in light in night mode. Synchronize illumination: Turn on to automatically synchronize the illumination with the surrounding light. The synchronization between day and night only works if the IR-cut filter is set to Auto or Off. Automatic illumination angle: Turn on to use the automatic illumination angle. Turn off to set the illumination angle manually. Illumination angle: Use the slider to manually set the illumination angle, for example, if the angle needs to be different from the camera’s angle of view. If the camera has a wide angle of view, you can set the illumination angle to a narrower angle, which equals a greater tele position. This will result in dark corners in the image. IR wavelength: Select the desired wavelength for the IR light. White light Allow illumination: Turn on to let the camera use white light in night mode. Synchronize illumination: Turn on to automatically synchronize the white light with the surrounding light. |
Exposure
Select an exposure mode to reduce rapidly changing irregular effects in the image, for example, flicker produced by different types of light sources. We recommend you to use the automatic exposure mode, or the same frequency as your power network.
Exposure mode:
Exposure zone: Use exposure zones to optimize the exposure in a selected part of the scene, for example, the area in front of an entrance door. Note The exposure zones are related to the original image (unrotated), and the names of the zones apply to the original image. This means, for example, that if the video stream is rotated 90°, then the Upper zone becomes the Right zone in the stream, and Left becomes Lower.
Max shutter: Select the shutter speed to provide the best image. Low shutter speeds (longer exposure) might cause motion blur when there is movement, and a too high shutter speed might affect the image quality. Max shutter works with max gain to improve the image. Max gain: Select the suitable max gain. If you increase the max gain, it improves the visible level of detail in dark images, but also increases the noise level. More noise can also result in increased use of bandwidth and storage. If you set the max gain to a high value, images can differ a lot if the light conditions are very different from day to night. Max gain works with max shutter to improve the image. Motion-adaptive exposure: Select to reduce motion blur in low-light conditions. Blur-noise trade-off: Use the slider to adjust the priority between motion blur and noise. If you want to prioritize low bandwidth and have less noise at the expense of details in moving objects, move the slider towards Low noise. If you want to prioritize the preservation of details in moving objects at the expense of noise and bandwidth, move the slider towards Low motion blur. Note You can change the exposure either by adjusting the exposure time or by adjusting the gain. If you increase the exposure time, it results in more motion blur, and if you increase the gain, it results in more noise. If you adjust the Blur-noise trade-off towards Low noise, the automatic exposure will prioritize longer exposure times over increasing gain, and the opposite if you adjust the trade-off towards Low motion blur. Both the gain and exposure time will eventually reach their maximum values in low-light conditions, regardless of the priority set. Lock aperture: Turn on to keep the aperture size set by the Aperture slider. Turn off to allow the camera to automatically adjust the aperture size. You can, for example, lock the aperture for scenes with permanent light conditions. Aperture: Use the slider to adjust the aperture size, that is, how much light passes through the lens. To allow more light to enter the sensor and thereby produce a brighter image in low-light conditions, move the slider towards Open. An open aperture also reduces the depth of field, which means that objects close to or far from the camera can appear unfocused. To allow more of the image to be in focus, move the slider towards Closed. Exposure level: Use the slider to adjust the image exposure. Defog: Turn on to detect the effects of foggy weather and automatically remove them for a clearer image. Note We recommend you not to turn on Defog in scenes with low contrast, large light level variations, or when the autofocus is slightly off. This can affect the image quality, for example, by increasing the contrast. Furthermore, too much light can negatively impact the image quality when defog is active. |
Optics
Temperature compensation: Turn on if you want the focus position to be corrected based on the temperature in the optics. IR compensation: Turn on if you want the focus position to be corrected when IR-cut filter is off and when there is IR light. Calibrate zoom and focus: Click to reset the optics and the zoom and focus settings to the factory default position. You need to do this if the optics have lost calibration during transport, or if the device has been exposed to extreme vibrations. |
Stream
General
Resolution: Select the image resolution suitable for the surveillance scene. A higher resolution increases bandwidth and storage. Frame rate: To avoid bandwidth problems on the network or reduce storage size, you can limit the frame rate to a fixed amount. If you leave the frame rate at zero, the frame rate is kept at the highest possible rate under the current conditions. A higher frame rate requires more bandwidth and storage capacity. P-frames: A P-frame is a predicted image that shows only the changes in the image from the previous frame. Enter the desired number of P-frames. The higher the number, the less bandwidth is required. However, if there is network congestion, there could be a noticeable deterioration in the video quality. Compression: Use the slider to adjust the image compression. High compression results in a lower bitrate and lower image quality. Low compression improves the image quality, but uses more bandwidth and storage when you record. Signed video: Turn on to add the signed video feature to the video. Signed video protects the video from tampering by adding cryptographic signatures to the video. |
Zipstream
Zipstream is a bitrate reduction technology, optimized for video surveillance, that reduces the average bitrate in an H.264, H.265, or AV1 stream in real time. Axis Zipstream applies a high bitrate in scenes where there are multiple regions of interest, for example, in scenes with moving objects. When the scene is more static, Zipstream applies a lower bitrate, and thereby reduces the required storage. To learn more, see Reducing the bit rate with Axis Zipstream
Optimize for storage: Turn on to minimize the bitrate while maintaining quality. The optimization does not apply to the stream shown in the web client. This can only be used if your VMS supports B-frames. Turning on Optimize for storage also turns on Dynamic GOP. Dynamic FPS (frames per second): Turn on to allow the bandwidth to vary based on the level of activity in the scene. More activity requires more bandwidth.
Dynamic GOP (Group of Pictures): Turn on to dynamically adjust the interval between I-frames based on the level of activity in the scene.
|
Bitrate control
|
Orientation
Mirror: Turn on to mirror the image. |
Overlays
: Click to add an overlay. Select the type of overlay from the dropdown list:
Widget: Meter: Show a bar chart that displays the most recently measured data value.
|
View areas
: Click to create a view area. Click the view area to access settings. Name: Enter a name for the view area. The maximum length is 64 characters. PTZ: Turn on to use pan, tilt, and zoom functionality in the view area. |
Privacy masks
: Click to create a new privacy mask. Privacy masks x/32 or Privacy masks x/100: Click this title bar to change the color of all privacy masks, or to delete all privacy masks permanently. Cell size: If you choose the mosaic color, the privacy masks appear as pixilated patterns. Use the slider to change the size of the pixels. Mask x: Click an individual mask name/number to rename, disable, or permanently delete that mask. Use zoom level: Turn on to make this privacy mask appear only when it reaches the zoom level at which it was created. Zooming out in the image hides the mask again. |
Audio
Add audio to your recording
- Turn on audio:
Go to Video > Stream > Audio and include audio.
If the device has more than one input source, select the correct one in Source.
Go to Audio > Device settings and turn on the correct input source.
If you make any changes to the input source, click Apply changes.
- Edit the stream profile that is used for the recording:
Go to System > Stream profiles and select the stream profile.
Select Include audio and turn it on.
Click Save.
Add audio capability to your product using portcast
With portcast technology, you can add audio capability to your product. It allows audio and I/O communication digitally over the network cable between the camera and the interface.
- To add audio capability to your Axis network video device, connect the portcast compatible Axis audio device and I/O Interface between your device and the PoE switch which provides power.
Connect the Axis network video device (1) and the Axis portcast device (2) with a PoE cable.
Connect the Axis portcast device (2) and the PoE switch (3) with a PoE cable.
- Axis network video device
- Axis portcast device
- Switch
Once the devices are connected, an audio tab becomes visible in the settings for your Axis network video device. Go to the audio tab and turn on Allow audio.
See your Axis portcast device’s user manual for more information.
Recordings
Click to filter the recordings. From: Show recordings done after a certain point in time. To: Show recordings up until a certain point in time. Source: Show recordings based on source. The source refers to the sensor. Event: Show recordings based on events. Storage: Show recordings based on storage type. |
Ongoing recordings: Show all ongoing recordings on the device. Start a recording on the device. Choose which storage device to save to. Stop a recording on the device. Triggered recordings will end when manually stopped or when the device is shut down. Continuous recordings will continue until manually stopped. Even if the device is shut down, the recording will continue when the device starts up again. |
Play the recording. Stop playing the recording. Show or hide information and options about the recording. Set export range: If you only want to export part of the recording, enter a time span. Note that if you work in a different time zone than the location of the device, the time span is based on the device’s time zone. Encrypt: Select to set a password for exported recordings. It will not be possible to open the exported file without the password. Click to delete a recording. Export: Export the whole or a part of the recording. |
Apps
Add app: Install a new app. Find more apps: Find more apps to install. You will be taken to an overview page of Axis apps. Allow unsigned apps: Turn on to allow installation of unsigned apps. View the security updates in AXIS OS and ACAP apps. Note The device’s performance might be affected if you run several apps at the same time. Use the switch next to the app name to start or stop the app. Open: Access the app’s settings. The available settings depend on the application. Some applications don’t have any settings. The context menu can contain one or more of the following options:
|
System
Time and location
Date and time
The time format depends on the web browser’s language settings.
We recommend you synchronize the device’s date and time with an NTP server.
Synchronization: Select an option for the device’s date and time synchronization.
Time zone: Select which time zone to use. Time will automatically adjust to daylight saving time and standard time.
Note The system uses the date and time settings in all recordings, logs, and system settings. |
Device location
Enter where the device is located. Your video management system can use this information to place the device on a map.
|
Network
IPv4
Assign IPv4 automatically: Select IPv4 automatic IP (DHCP) to let the network assign your IP address, subnet mask, and router automatically, without manual configuration. We recommend using automatic IP assignment (DHCP) for most networks. IP address: Enter a unique IP address for the device. Static IP addresses can be assigned at random within isolated networks, provided that each address is unique. To avoid conflicts, we recommend you contact your network administrator before you assign a static IP address. Subnet mask: Enter the subnet mask to define what addresses are inside the local area network. Any address outside the local area network goes through the router. Router: Enter the IP address of the default router (gateway) used to connect devices that are attached to different networks and network segments. Fallback to static IP address if DHCP isn’t available: Select if you want to add a static IP address to use as fallback if DHCP is unavailable and can’t assign an IP address automatically. Note If DHCP isn’t available and the device uses a static address fallback, the static address is configured with a limited scope. |
IPv6
Assign IPv6 automatically: Select to turn on IPv6 and to let the network router assign an IP address to the device automatically. |
Hostname
Assign hostname automatically: Select to let the network router assign a hostname to the device automatically. Hostname: Enter the hostname manually to use as an alternative way of accessing the device. The server report and system log use the hostname. Allowed characters are A–Z, a–z, 0–9 and -. Enable dynamic DNS updates: Allow your device to automatically update its domain name server records whenever its IP address changes. Register DNS name: Enter a unique domain name that points to your device's IP address. Allowed characters are A–Z, a–z, 0–9 and -. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) sets how long a DNS record stays valid before it needs to be updated. |
DNS servers
Assign DNS automatically: Select to let the DHCP server assign search domains and DNS server addresses to the device automatically. We recommend automatic DNS (DHCP) for most networks. Search domains: When you use a hostname that is not fully qualified, click Add search domain and enter a domain in which to search for the hostname the device uses. DNS servers: Click Add DNS server and enter the IP address of the DNS server. This provides the translation of hostnames to IP addresses on your network. |
If DHCP is disabled, features that rely on automatic network configuration, such as hostname, DNS servers, NTP, and others, may stop working.
HTTP and HTTPS
HTTPS is a protocol that provides encryption for page requests from users and for the pages returned by the web server. The encrypted exchange of information is governed by the use of an HTTPS certificate, which guarantees the authenticity of the server.
To use HTTPS on the device, you must install an HTTPS certificate. Go to System > Security to create and install certificates.
Allow access through: Select if a user is allowed to connect to the device through the HTTP, HTTPS, or both HTTP and HTTPS protocols. Note If you view encrypted web pages through HTTPS, you might experience a drop in performance, especially when you request a page for the first time. HTTP port: Enter the HTTP port to use. The device allows port 80 or any port in the range 1024-65535. If you are logged in as an administrator, you can also enter any port in the range 1-1023. If you use a port in this range, you get a warning. HTTPS port: Enter the HTTPS port to use. The device allows port 443 or any port in the range 1024-65535. If you are logged in as an administrator, you can also enter any port in the range 1-1023. If you use a port in this range, you get a warning. Certificate: Select a certificate to enable HTTPS for the device. |
Global proxies
Http proxy: Specify a global proxy host or IP address according to the allowed format. Https proxy: Specify a global proxy host or IP address according to the allowed format.
Note Restart the device to apply the global proxy settings.
|
Network discovery protocols
Bonjour®: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. Bonjour name: Enter a friendly name to be visible on the network. The default name is the device name and MAC address. UPnP®: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. UPnP name: Enter a friendly name to be visible on the network. The default name is the device name and MAC address. WS-Discovery: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. LLDP and CDP: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. Turning LLDP and CDP off can impact the PoE power negotiation. To resolve any issues with the PoE power negotiation, configure the PoE switch for hardware PoE power negotiation only. |
One-click cloud connection
One-click cloud connection (O3C) together with an O3C service provides easy and secure internet access to live and recorded video from any location. For more information, see axis.com/end-to-end-solutions/hosted-services.
Allow O3C:
Proxy settings: If needed, enter the proxy settings to connect to the proxy server. Host: Enter the proxy server’s address. Port: Enter the port number used for access. Login and Password: If needed, enter username and password for the proxy server. Authentication method:
Owner authentication key (OAK): Click Get key to fetch the owner authentication key. This is only possible if the device is connected to the internet without a firewall or proxy. |
SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) allows remote management of network devices.
SNMP: Select the version of SNMP to use.
Note All Axis Video MIB traps are enabled when you turn on SNMP v1 and v2c traps. For more information, see AXIS OS Portal > SNMP.
|
Security
Certificates
Certificates are used to authenticate devices on a network. The device supports two types of certificates:
These formats are supported:
Important If you reset the device to factory default, all certificates are deleted. Any pre-installed CA certificates are reinstalled. Add certificate : Click to add a certificate. A step-by-step guide opens up.
The context menu contains:
Secure keystore:
|
Network access control and encryption
IEEE 802.1x IEEE 802.1x is an IEEE standard for port-based network admission control providing secure authentication of wired and wireless network devices. IEEE 802.1x is based on EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol). To access a network protected by IEEE 802.1x, network devices must authenticate themselves. The authentication is performed by an authentication server, typically a RADIUS server (for example, FreeRADIUS and Microsoft Internet Authentication Server). IEEE 802.1AE MACsec IEEE 802.1AE MACsec is an IEEE standard for media access control (MAC) security that defines connectionless data confidentiality and integrity for media access independent protocols. Certificates When configured without a CA certificate, server certificate validation is disabled and the device tries to authenticate itself regardless of what network it is connected to. When using a certificate, in Axis' implementation, the device and the authentication server authenticate themselves with digital certificates using EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security). To allow the device to access a network protected through certificates, you must install a signed client certificate on the device. Authentication method: Select an EAP type used for authentication. Client certificate: Select a client certificate to use IEEE 802.1x. The authentication server uses the certificate to validate the client’s identity. CA certificates: Select CA certificates to validate the authentication server’s identity. When no certificate is selected, the device tries to authenticate itself regardless of what network it is connected to. EAP identity: Enter the user identity associated with the client certificate. EAPOL version: Select the EAPOL version that is used in the network switch. Use IEEE 802.1x: Select to use the IEEE 802.1x protocol. These settings are only available if you use IEEE 802.1x PEAP-MSCHAPv2 as the authentication method:
These settings are only available if you use IEEE 802.1ae MACsec (Static CAK/Pre-Shared Key) as the authentication method:
|
Prevent brute-force attacks
Blocking: Turn on to block brute-force attacks. A brute-force attack uses trial-and-error to guess login info or encryption keys. Blocking period: Enter the number of seconds to block a brute-force attack. Blocking conditions: Enter the number of authentication failures allowed per second before the block starts. You can set the number of failures allowed both on page level and device level. |
Firewall
Firewall: Turn on to activate the firewall.
To make exceptions to the default policy, you can create rules that allows or blocks connections to the device from specific addresses, protocols, and ports. + New rule: Click to create a rule.
LIMIT: Select to accept connections from devices that match the criteria defined in the rule but apply limits to reduce excessive traffic.
Test rules: Click to test the rules that you have defined.
|
Custom signed AXIS OS certificate
To install test software or other custom software from Axis on the device, you need a custom signed AXIS OS certificate. The certificate verifies that the software is approved by both the device owner and Axis. The software can only run on a specific device which is identified by its unique serial number and chip ID. Only Axis can create custom signed AXIS OS certificates, since Axis holds the key to sign them. Install: Click to install the certificate. You need to install the certificate before you install the software. The context menu contains:
|
Accounts
Accounts
Add account: Click to add a new account. You can add up to 100 accounts. Account: Enter a unique account name. New password: Enter a password for the account. Passwords must be 1 to 64 characters long. Only ASCII printable characters (code 32 to 126) are allowed in the password, for example, letters, numbers, punctuation, and some symbols. Repeat password: Enter the same password again. Privileges:
The context menu contains: Update account: Edit the account properties. Delete account: Delete the account. You can’t delete the root account. |
Anonymous access
Allow anonymous viewing: Turn on to allow anyone access the device as a viewer without logging in with an account. Allow anonymous PTZ operating: Turn on to allow anonymous users to pan, tilt, and zoom the image. |
SSH accounts
Add SSH account: Click to add a new SSH account.
Account: Enter a unique account name. New password: Enter a password for the account. Passwords must be 1 to 64 characters long. Only ASCII printable characters (code 32 to 126) are allowed in the password, for example, letters, numbers, punctuation, and some symbols. Repeat password: Enter the same password again. Comment: Enter a comment (optional). The context menu contains: Update SSH account: Edit the account properties. Delete SSH account: Delete the account. You can’t delete the root account. |
Virtual host
Add virtual host: Click to add a new virtual host. Enabled: Select to use this virtual host. Server name: Enter the name of the server. Only use numbers 0-9, letters A-Z, and hyphen (-). Port: Enter the port the server is connected to. Type: Select the type of authentication to use. Select between Basic, Digest, Open ID, and Client Credential Grant. HTTPS: Select to use HTTPS. The context menu contains:
|
OpenID Configuration
If you can't use OpenID to sign in, use the Digest or Basic credentials you used when you configured OpenID to sign in.
Client ID: Enter the OpenID username. Outgoing Proxy: Enter the proxy address for the OpenID connection to use a proxy server. Admin claim: Enter a value for the admin role. Provider URL: Enter the web link for the API endpoint authentication. Format should be https://[insert URL]/.well-known/openid-configuration Operator claim: Enter a value for the operator role. Require claim: Enter the data that should be in the token. Viewer claim: Enter the value for the viewer role. Remote user: Enter a value to identify remote users. This assists to display the current user in the device’s web interface. Scopes: Optional scopes that could be part of the token. Client secret: Enter the OpenID password Save: Click to save the OpenID values. Enable OpenID: Turn on to close current connection and allow device authentication from the provider URL. |
Events
Rules
A rule defines the conditions that triggers the product to perform an action. The list shows all the currently configured rules in the product.
You can create up to 256 action rules.
Add a rule: Create a rule. Name: Enter a name for the rule. Wait between actions: Enter the minimum time (hh:mm:ss) that must pass between rule activations. It is useful if the rule is activated by, for example, day-night mode conditions, to avoid that small light changes during sunrise and sunset activate the rule repeatedly. Condition: Select a condition from the list. A condition must be met for the device to perform an action. If multiple conditions are defined, all of them must be met to trigger the action. For information about specific conditions, see Get started with rules for events. Use this condition as a trigger: Select to make this first condition function only as a starting trigger. It means that once the rule is activated, it remains active for as long as all the other conditions are met, no matter the state of the first condition. If you don’t select this option, the rule will simply be active whenever all the conditions are met. Invert this condition: Select if you want the condition to be the opposite of your selection. Add a condition: Click to add an additional condition. Action: Select an action from the list and enter its required information. For information about specific actions, see Get started with rules for events. |
Recipients
You can set up your device to notify recipients about events or send files.
If you set up your device to use FTP or SFTP, don’t change or remove the unique sequence number that’s added to the file names. If you do that, only one image per event can be sent.
The list shows all the recipients currently configured in the product, along with information about their configuration.
You can create up to 20 recipients.
Add a recipient: Click to add a recipient. Name: Enter a name for the recipient. Type: Select from the list:
Test: Click to test the setup. The context menu contains: View recipient: Click to view all the recipient details. Copy recipient: Click to copy a recipient. When you copy, you can make changes to the new recipient. Delete recipient: Click to delete the recipient permanently. |
Schedules
Schedules and pulses can be used as conditions in rules. The list shows all the schedules and pulses currently configured in the product, along with information about their configuration. Add schedule: Click to create a schedule or pulse. |
Manual triggers
You can use the manual trigger to manually trigger a rule. The manual trigger can, for example, be used to validate actions during product installation and configuration. |
MQTT
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a standard messaging protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT). It was designed for simplified IoT integration and is used in a wide variety of industries to connect remote devices with a small code footprint and minimal network bandwidth. The MQTT client in Axis device software can simplify integration of data and events produced in the device to systems which are not video management software (VMS). Set up the device as an MQTT client. MQTT communication is based on two entities, the clients and the broker. The clients can send and receive messages. The broker is responsible for routing messages between clients. You can learn more about MQTT in AXIS OS Knowledge base. |
ALPN
ALPN is a TLS/SSL extension that allows for the selection of an application protocol during the handshake phase of the connection between the client and server. This is used to enable MQTT traffic over the same port that is used for other protocols, such as HTTP. In some cases, there might not be a dedicated port open for MQTT communication. A solution in such cases is to use ALPN to negotiate the use of MQTT as the application protocol on a standard port, allowed by the firewalls. |
MQTT client
Connect: Turn on or off the MQTT client. Status: Shows the current status of the MQTT client. Broker Host: Enter the hostname or IP address of the MQTT server. Protocol: Select which protocol to use. Port: Enter the port number.
ALPN protocol: Enter the ALPN protocol name provided by your MQTT broker provider. This is only applicable with MQTT over SSL and MQTT over WebSocket Secure. Username: Enter the username that the client will use to access the server. Password: Enter a password for the username. Client ID: Enter a client ID. The client identifier is sent to the server when the client connects to it. Clean session: Controls the behavior at connection and disconnection time. When selected, the state information is discarded at connect and disconnect. HTTP proxy: A URL with a maximum length of 255 bytes. You can leave the field empty if you don't want to use an HTTP proxy. HTTPS proxy: A URL with a maximum length of 255 bytes. You can leave the field empty if you don't want to use an HTTPS proxy. Keep alive interval: Enables the client to detect when the server is no longer available without having to wait for the long TCP/IP timeout. Timeout: The time interval in seconds to allow a connect to complete. Default value: 60 Device topic prefix: Used in the default values for the topic in the connect message and LWT message on the MQTT client tab, and in the publication conditions on the MQTT publication tab. Reconnect automatically: Specifies whether the client should reconnect automatically after a disconnect. Connect message Specifies if a message should be sent out when a connection is established. Send message: Turn on to send messages. Use default: Turn off to enter your own default message. Topic: Enter the topic for the default message. Payload: Enter the content for the default message. Retain: Select to keep the state of client on this Topic QoS: Change the QoS layer for the packet flow. Last Will and Testament message The Last Will Testament (LWT) lets a client provide a testament along with its credentials when connecting to the broker. If the client disconnects ungracefully at some point later (maybe because his power source died), it can let the broker deliver a message to other clients. This LWT message has the same form as an ordinary message and gets routed via the same mechanics. Send message: Turn on to send messages. Use default: Turn off to enter your own default message. Topic: Enter the topic for the default message. Payload: Enter the content for the default message. Retain: Select to keep the state of client on this Topic QoS: Change the QoS layer for the packet flow. |
MQTT publication
Use default topic prefix: Select to use the default topic prefix, that is defined in the device topic prefix in the MQTT client tab. Include condition: Select to include the topic that describes the condition in the MQTT topic. Include namespaces: Select to include ONVIF topic namespaces in the MQTT topic. Include serial number: Select to include the device’s serial number in the MQTT payload. Add condition: Click to add a condition. Retain: Defines which MQTT messages are sent as retained.
QoS: Select the desired level for the MQTT publication. |
MQTT subscriptions
Add subscription: Click to add a new MQTT subscription. Subscription filter: Enter the MQTT topic that you want to subscribe to. Use device topic prefix: Add the subscription filter as prefix to the MQTT topic. Subscription type:
QoS: Select the desired level for the MQTT subscription. |
MQTT overlays
Note Connect to an MQTT broker before you add MQTT overlay modifiers. Add overlay modifier: Click to add a new overlay modifier. Topic filter: Add the MQTT topic that contains the data you want to show in the overlay. Data field: Specify the key for the message payload that you want to show in the overlay, assuming the message is in JSON format.
|
Storage
Network storage
Network storage: Turn on to use network storage. Add network storage: Click to add a network share where you can save recordings.
Remove network storage: Click to unmount, unbind, and remove the connection to the network share. This removes all settings for the network share. Unbind: Click to unbind and disconnect the network share. Unmount: Click to unmount the network share. Write protect: Turn on to stop writing to the network share and protect recordings from being removed. You can’t format a write-protected network share. Retention time: Select how long to keep recordings, to limit the amount of old recordings, or to comply with regulations regarding data storage. If the network storage becomes full, old recordings are removed before the selected time period passes. Tools
|
Onboard storage
Important Risk of data loss and corrupted recordings. Do not remove the SD card while the device is running. Unmount the SD card before you remove it. Unmount: Click to safely remove the SD card. Write protect: Turn on to stop writing to the SD card and protect recordings from being removed. You can’t format a write-protected SD card. Autoformat: Turn on to automatically format a newly inserted SD card. It formats the file system into ext4. Ignore: Turn on to stop storing recordings on the SD card. When you ignore the SD card, the device no longer recognizes that the card exists. The setting is only available to administrators. Retention time: Select how long to keep recordings to limit the amount of old recordings or comply with data storage regulations. When the SD card is full, it deletes old recordings before their retention time has passed. Tools
Wear trigger: Set a value for the SD card wear level at which you want to trigger an action. The wear level ranges from 0–200%. A new SD card that has never been used has a wear level of 0%. A wear level of 100% indicates that the SD card is close to its expected lifetime. When the wear-level reaches 200%, there is a high risk of the SD card malfunctioning. We recommend setting the wear trigger between 80–90%. This gives you time to download any recordings as well as replace the SD card in time before it potentially wears out. The wear trigger allows you to set up an event and get a notification when the wear level reaches your set value. |
SIP
Settings
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is used for interactive communication sessions between users. The sessions can include audio and video.
SIP setup assistant: Click to set up and configure SIP step by step. Enable SIP: Check this option to make it possible to initiate and receive SIP calls. Allow incoming calls: Check this option to allow incoming calls from other SIP devices.
|
Accounts
All current SIP accounts are listed under SIP accounts. For registered accounts, the colored circle lets you know the status.
The peer to peer (default) account is an automatically created account. You can delete it if you create at least one other account and set that account as default. The default account is always used when a VAPIX® Application Programming Interface (API) call is made without specifying which SIP account to call from.
|
DTMF
Add sequence: Click to create a new dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) sequence. To create a rule that is activated by touch-tone, go to Events > Rules. Sequence: Enter the characters to activate the rule. Allowed characters: 0–9, A-D, #, and *. Description: Enter a description of the action to be triggered by the sequence. Accounts: Select the accounts that will use the DTMF sequence. If you choose peer-to-peer, all peer-to-peer accounts will share the same DTMF sequence. |
Protocols Select the protocols to use for each account. All peer-to-peer accounts share the same protocol settings. Use RTP (RFC2833): Turn on to allow dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) signaling, other tone signals and telephony events in RTP packets. Use SIP INFO (RFC2976): Turn to include the INFO method to the SIP protocol. The INFO method adds optional application layer information, generally related to the session. |
Test call
SIP account: Select which account to make the test call from. SIP address: Enter a SIP address and click to make a test call and verify that the account works. |
Access list
Use access list: Turn on to restrict who can make calls to the device.
Add source: Click to create a new entry in the access list. SIP source: Type the caller ID or SIP server address of the source. |
Stream profiles
A stream profile is a group of settings that affect the video stream. You can use stream profiles in different situations, for example, when you create events and use rules to record.
Add stream profile: Click to create a new stream profile. Preview: A preview of the video stream with the stream profile settings you select. The preview updates when you change the settings on the page. If your device has different view areas, you can change the view area in the drop-down in the bottom left corner of the image. Name: Add a name for your profile. Description: Add a description of your profile. Video codec: Select the video codec that should apply for the profile. Resolution: See Stream for a description of this setting. Frame rate: See Stream for a description of this setting. Compression: See Stream for a description of this setting. Zipstream: See Stream for a description of this setting. Optimize for storage: See Stream for a description of this setting. Dynamic FPS: See Stream for a description of this setting. Dynamic GOP: See Stream for a description of this setting. Mirror: See Stream for a description of this setting. GOP length: See Stream for a description of this setting. Bitrate control: See Stream for a description of this setting. Include overlays: Select what type of overlays to include. See Overlays for information about how to add overlays. Include audio: See Stream for a description of this setting. |
ONVIF
ONVIF accounts
ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) is a global interface standard that makes it easier for end-users, integrators, consultants, and manufacturers to take advantage of the possibilities offered by network video technology. ONVIF enables interoperability between different vendor products, increased flexibility, reduced cost and future-proof systems.
When you create an ONVIF account, you automatically enable ONVIF communication. Use the account name and password for all ONVIF communication with the device. For more information see the Axis Developer Community at axis.com.
Add accounts: Click to add a new ONVIF account. Account: Enter a unique account name. New password: Enter a password for the account. Passwords must be 1 to 64 characters long. Only ASCII printable characters (code 32 to 126) are allowed in the password, for example, letters, numbers, punctuation, and some symbols. Repeat password: Enter the same password again. Privileges:
The context menu contains: Update account: Edit the account properties. Delete account: Delete the account. You can’t delete the root account. |
ONVIF media profiles
An ONVIF media profile consists of a set of configurations that you can use to change media stream settings. You can create new profiles with your own set of configurations or use preconfigured profiles for a quick setup.
Add media profile: Click to add a new ONVIF media profile. Profile name: Add a name for the media profile. Video source: Select the video source for your configuration.
Video encoder: Select the video encoding format for your configuration.
Note Enable audio in the device to get the option to select an audio source and audio encoder configuration. Audio source: Select the audio input source for your configuration.
Audio encoder: Select the audio encoding format for your configuration.
Audio decoder: Select the audio decoding format for your configuration.
Audio output: Select the audio output format for your configuration.
Metadata: Select the metadata to include in your configuration.
PTZ: Select the PTZ settings for your configuration.
Create: Click to save your settings and create the profile. Cancel: Click to cancel the configuration and clear all settings. profile_x: Click on the profile name to open and edit the preconfigured profile. |
Analytics metadata
RTSP metadata producers
View and manage the data channels that stream metadata and the channels they use.
These settings are for the RTSP metadata stream that uses ONVIF XML. Changes made here don't affect the Metadata visualization page.
Producer: A data channel that uses Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) to send metadata. Channel: The channel used to send metadata from a producer. Turn on to enable the metadata stream. Turn off for compatibility or resource management reasons. |
Detectors
Camera tampering
The camera tampering detector generates an alarm when the scene changes, for example, when the lens is covered, sprayed or severely put out of focus, and the time in Trigger delay has passed. The tampering detector only activates when the camera has not moved for at least 10 seconds. During this period, the detector sets up a scene model to use as a comparison to detect tampering in current images. For the scene model to be set up properly, make sure that the camera is in focus, the lighting conditions are correct, and the camera doesn’t point at a scene that lacks contours, for example, a blank wall. Camera tampering can be used as a condition to trigger actions.
Trigger delay: Enter the minimum time that the tampering conditions must be active before the alarm triggers. This can help prevent false alarms for known conditions that affect the image. Trigger on dark images: It is very difficult to generate alarms when the camera lens is sprayed, since it is impossible to distinguish that event from other situations where the image turns dark in a similar way, for example, when the lighting conditions change. Turn on this parameter to generate alarms for all cases where the image turns dark. When it’s turned off, the device doesn’t generate any alarm when the image turns dark. Note For detection of tampering attempts in static and non-crowded scenes. |
Video out
Logs
Reports and logs
Reports
Logs
|
Network trace
Important A network trace file might contain sensitive information, for example certificates or passwords. A network trace file can help you troubleshoot problems by recording activity on the network. Trace time: Select the duration of the trace in seconds or minutes, and click Download. |
Remote system log
Syslog is a standard for message logging. It allows separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, which indicates the software type generating the message, and assigned a severity level.
Server: Click to add a new server. Host: Enter the hostname or IP address of the server. Format: Select which syslog message format to use.
Protocol: Select the protocol to use:
Port: Edit the port number to use a different port. Severity: Select which messages to send when triggered. Type: Select the type of logs you want to send. Test server setup: Send a test message to all servers before you save the settings. CA certificate set: See the current settings or add a certificate. |
Plain config
Plain config is for advanced users with experience of Axis device configuration. Most parameters can be set and edited from this page. |
Maintenance
Restart: Restart the device. This does not affect any of the current settings. Running applications restart automatically. Restore: Return most settings to the factory default values. Afterwards you must reconfigure the device and apps, reinstall any apps that didn’t come preinstalled, and recreate any events and presets. Important The only settings saved after restore are:
Factory default: Return all settings to the factory default values. Afterwards you must reset the IP address to make the device accessible. Note All Axis device software is digitally signed to ensure that you only install verified software on your device. This further increases the overall minimum cybersecurity level of Axis devices. For more information, see the white paper “Axis Edge Vault” at axis.com. AXIS OS upgrade: Upgrade to a new AXIS OS version. New releases can contain improved functionality, bug fixes, and completely new features. We recommend you to always use the latest AXIS OS release. To download the latest release, go to axis.com/support.
AXIS OS rollback: Revert to the previously installed AXIS OS version. |
Learn more
View area
A view area is a cropped part of the full view. You can stream and store view areas instead of the full view to minimize bandwidth and storage needs. If you enable PTZ for a view area, you can pan, tilt and zoom within it. By using view areas you can remove parts of the full view, for example, the sky.
When you set up a view area, we recommend you to set the video stream resolution to the same size as or smaller than the view area size. If you set the video stream resolution larger than the view area size it implies digitally scaled up video after sensor capture, which requires more bandwidth without adding image information.
Overlays
Overlays are superimposed over the video stream. They are used to provide extra information during recordings, such as a timestamp, or during product installation and configuration. You can add either text or an image.
Streaming and storage
Video compression formats
Decide which compression method to use based on your viewing requirements, and on the properties of your network. The available options are:
Motion JPEG
Motion JPEG, or MJPEG, is a digital video sequence that is made up of a series of individual JPEG images. These images are then displayed and updated at a rate sufficient to create a stream that shows constantly updated motion. For the viewer to perceive motion video the rate must be at least 16 image frames per second. Full motion video is perceived at 30 (NTSC) or 25 (PAL) frames per second.
The Motion JPEG stream uses considerable amounts of bandwidth, but provides excellent image quality and access to every image contained in the stream.
H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10/AVC
H.264 is a licensed technology. The Axis product includes one H.264 viewing client license. To install additional unlicensed copies of the client is prohibited. To purchase additional licenses, contact your Axis reseller.
H.264 can, without compromising image quality, reduce the size of a digital video file by more than 80% compared to the Motion JPEG format and by as much as 50% compared to older MPEG formats. This means that less network bandwidth and storage space are required for a video file. Or seen another way, higher video quality can be achieved for a given bitrate.
Bitrate control
Bitrate control helps you to manage the bandwidth consumption of your video stream.
Variable bitrate (VBR)
Variable bitrate allows the bandwidth consumption to vary depending on the level of activity in the scene. The more activity, the more bandwidth you need. With variable bitrate you are guaranteed constant image quality, but you need to make sure you have storage margins.
Maximum bitrate (MBR)
Maximum bitrate lets you set a target bitrate to handle bitrate limitations in your system. You might see a decline in image quality or frame rate as the instantaneous bitrate is kept below the specified target bitrate. You can choose to prioritize either image quality or frame rate. We recommend that you configure the target bitrate to a higher value than the expected bitrate. This gives you a margin in case there is a high level of activity in the scene.
- Target bitrate
Average bitrate (ABR)
With average bitrate, the bitrate is automatically adjusted over a longer period of time. This is so you can meet the specified target and provide the best video quality based on your available storage. Bitrate is higher in scenes with a lot of activity, compared to static scenes. You are more likely to get better image quality when in scenes with a lot of activity if you use the average bitrate option. You can define the total storage required to store the video stream for a specified amount of time (retention time) when image quality is adjusted to meet the specified target bitrate. Specify the average bitrate settings in one of the following ways:
To calculate the estimated storage need, set the target bitrate and the retention time.
To calculate the average bitrate, based on available storage and required retention time, use the target bitrate calculator.
- Target bitrate
- Actual average bitrate
- You can also turn on maximum bitrate and specify a target bitrate within the average bitrate option.
- Target bitrate
- Actual average bitrate
Analytics and apps
With analytics and apps you can get more out of your Axis device. AXIS Camera Application Platform (ACAP) is an open platform that makes it possible for third parties to develop analytics and other apps for Axis devices. Apps can be preinstalled on the device, available for download for free, or for a license fee.
To find the user manuals for Axis analytics and apps, go to help.axis.com.
- Several apps can run at the same time but some apps might not be compatible with each other. Certain combinations of apps might require too much processing power or memory resources when run in parallel. Verify that the apps work together before deployment.
Troubleshooting
Reset to factory default settings
![]() Possibly hazardous optical radiation is emitted from this product. It can be harmful to the eyes. Don’t stare at the operating lamp.
Possibly hazardous optical radiation is emitted from this product. It can be harmful to the eyes. Don’t stare at the operating lamp.
Reset to factory default should be used with caution. A reset to factory default resets all settings, including the IP address, to the factory default values.
To reset the product to the factory default settings:
Disconnect power from the product.
Press and hold the control button while reconnecting power. See Product overview.
Keep the control button pressed for 15–30 seconds until the status LED indicator flashes amber.
Release the control button. The process is complete when the status LED indicator turns green. If no DHCP server is available on the network, the device IP address will default to one of the following:
Devices with AXIS OS 12.0 and later: Obtained from the link-local address subnet (169.254.0.0/16)
Devices with AXIS OS 11.11 and earlier: 192.168.0.90/24
Use the installation and management software tools to assign an IP address, set the password, and access the device.
The installation and management software tools are available from the support pages on axis.com/support.
You can also reset parameters to factory default through the device’s web interface. Go to Maintenance > Factory default and click Default.
Check the current AXIS OS version
AXIS OS determines the functionality of our devices. When you troubleshoot a problem, we recommend that you to start by checking the current AXIS OS version. The latest version might contain a correction that fixes your particular problem.
To check the current AXIS OS version:
Go to the device’s web interface > Status.
Under Device info, see the AXIS OS version.
Upgrade AXIS OS
- When you upgrade the device software, your preconfigured and customized settings are saved. Axis Communications AB can't guarantee that the settings are saved, even if the features are available in the new AXIS OS version.
- Starting from AXIS OS 12.6, you must install every LTS version between your device’s current version and the target version. For example, if the currently installed device software version is AXIS OS 11.2, you have to install the LTS version AXIS OS 11.11 before you can upgrade the device to AXIS OS 12.6. For more information, see AXIS OS Portal: Upgrade path.
- Make sure the device remains connected to the power source throughout the upgrade process.
- When you upgrade the device with the latest AXIS OS version in the active track, the product receives the latest functionality available. Always read the upgrade instructions and release notes available with each new release before you upgrade. To find the latest AXIS OS version and the release notes, go to axis.com/support/device-software.
Download the AXIS OS file to your computer, available free of charge at axis.com/support/device-software.
Log in to the device as an administrator.
Go to Maintenance > AXIS OS upgrade and click Upgrade.
- When the upgrade has finished, the product restarts automatically.
You can use AXIS Device Manager to upgrade multiple devices at the same time. Find out more at axis.com/products/axis-device-manager.
Technical problems and possible solutions
Problems upgrading AXIS OS
AXIS OS upgrade failed If the upgrade fails, the device reloads the previous version. The most common reason is that the wrong AXIS OS file has been uploaded. Check that the name of the AXIS OS file corresponds to your device and try again. |
Problems after AXIS OS upgrade If you experience problems after the upgrade, roll back to the previously installed version from the Maintenance page. |
Problems setting the IP address
Can’t set the IP address
|
Problems accessing the device
Can’t log in when accessing the device from a browser When HTTPS is enabled, make sure that you use the correct protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) when you try to log in. You might need to manually type If you’ve lost the password for the root account, you must reset the device to the factory default settings. For instructions, see Reset to factory default settings. |
The IP address has been changed by DHCP IP addresses obtained from a DHCP server are dynamic and could change. If the IP address has been changed, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager to locate the device on the network. Identify the device using its model or serial number, or by the DNS name (if the name has been configured). If required, you can assign a static IP address manually. For instructions, go to axis.com/support. |
Certificate error when using IEEE 802.1X For authentication to work properly, the date and time settings in the Axis device must be synchronized with an NTP server. Go to System > Date and time. |
The browser isn’t supported For a list of recommended browsers, see Browser support. |
Can’t access the device externally To access the device externally, we recommend you to use one of the following applications for Windows®:
For instructions and download, go to axis.com/vms. |
Problems with streaming
Multicast H.264 only accessible by local clients Check if your router supports multicasting, or if you need to configure the router settings between the client and the device. You might need to increase the TTL (Time To Live) value. |
No multicast H.264 displayed in the client Check with your network administrator that the multicast addresses used by the Axis device are valid for your network. Check with your network administrator to see if there is a firewall that prevents viewing. |
Poor rendering of H.264 images Ensure that your graphics card uses the latest driver. You can usually download the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website. |
Color saturation is different in H.264 and Motion JPEG Modify the settings for your graphics adapter. Check the adapter’s documentation for more information. |
Lower frame rate than expected
|
Can't select H.265 encoding in live view Web browsers don’t support H.265 decoding. Use a video management system or application that supports H.265 decoding. |
Problems with MQTT
Can’t connect over port 8883 with MQTT over SSL The firewall blocks traffic that uses port 8883 since it’s regarded insecure. In some cases the server/broker might not provide a specific port for MQTT communication. It might still be possible to use MQTT over a port normally used for HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
|
Problems with operating the device
Front heater and wiper aren’t working If the front heater or wiper are not turning on, confirm that the top cover is properly fastened to the bottom of the housing unit. |
If you can’t find what you’re looking for here, try the troubleshooting section at axis.com/support.
Performance considerations
When you set up your system, it’s important to consider how different settings and situations affect performance. Some factors affect bandwidth (bitrate), others affect frame rate, and some affect both.
The most important factors to consider:
High image resolution or lower compression levels result in images containing more data which in turn affects the bandwidth.
Rotating the image in the GUI can increase the product's CPU load.
Access by large numbers of Motion JPEG clients or unicast H.264/H.265/AV1 clients affects the bandwidth.
Simultaneous viewing of different streams (resolution, compression) by different clients affects both frame rate and bandwidth.
Use identical streams wherever possible to maintain a high frame rate. Stream profiles can be used to ensure that streams are identical.
Accessing video streams with different codecs simultaneously affects both frame rate and bandwidth. For optimal performance, use streams with the same codec.
Heavy usage of event settings affects the product’s CPU load which in turn affects the frame rate.
Using HTTPS may reduce frame rate, in particular if streaming Motion JPEG.
Heavy network utilization due to poor infrastructure affects the bandwidth.
Viewing on poorly performing client computers lowers perceived performance and affects frame rate.
Running multiple AXIS Camera Application Platform (ACAP) applications simultaneously may affect the frame rate and the general performance.
Contact support
If you need more help, go to axis.com/support.
Specifications
Product overview
AXIS P3227-LV and AXIS P3228-LV
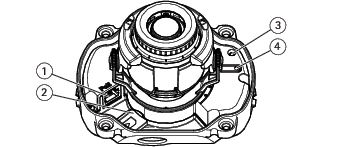
- Network connector (PoE)
- SD memory card slot
- Status LED indicator
- Control button
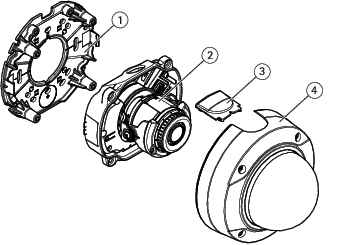
- Mounting bracket
- Camera unit
- Lid
- Dome
AXIS P3227-LVE and AXIS P3228-LVE
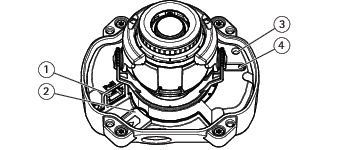
- Network connector (PoE)
- SD memory card slot
- Status LED indicator
- Control button
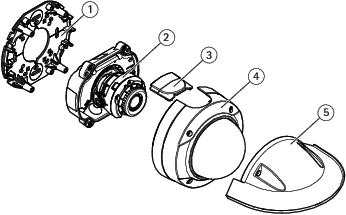
- Mounting bracket
- Camera unit
- Lid
- Dome
- Weather shield
LED Indicators
| Status LED | Indication |
| Unlit | Connection and normal operation. |
| Green | Steady green for 10 seconds for normal operation after startup completed. |
| Amber | Steady during startup. Flashes during firmware upgrade or reset to factory default. |
| Amber/Red | Flashes amber/red if network connection is unavailable or lost. |
SD card slot
- Risk of damage to SD card. Don’t use sharp tools, metal objects, or excessive force when inserting or removing the SD card. Use your fingers to insert and remove the card.
- Risk of data loss and corrupted recordings. Unmount the SD card from the device’s web interface before removing it. Don’t remove the SD card while the product is running.
This device supports microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC cards.
For SD card recommendations, see axis.com.
![]()
![]()
![]() microSD, microSDHC, and microSDXC Logos are trademarks of SD-3C LLC. microSD, microSDHC, microSDXC are trademarks or registered trademarks of SD-3C, LLC in the United States, other countries or both.
microSD, microSDHC, and microSDXC Logos are trademarks of SD-3C LLC. microSD, microSDHC, microSDXC are trademarks or registered trademarks of SD-3C, LLC in the United States, other countries or both.
Buttons
Control button
- The control button is used for:
Resetting the product to factory default settings. See Reset to factory default settings.
Connectors
Network connector
RJ45 Ethernet connector with Power over Ethernet (PoE).