Solution overview
The network door controller can easily be connected to and powered by your existing IP network with no need for special cabling.
Each network door controller is an intelligent device that is easily mounted close to a door. It can power and control up to two readers.
Installation
Get started
Find the device on the network
To find Axis devices on the network and assign them IP addresses in Windows®, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager. Both applications are free and can be downloaded from axis.com/support.
For more information about how to find and assign IP addresses, go to How to assign an IP address and access your device.
Browser support
You can use the device with the following browsers:
ChromeTM | EdgeTM | Firefox® | Safari® | |
Windows® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
macOS® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
Linux® | ✓ | ✓ | * | * |
Other operating systems | * | * | * | * |
✓: Recommended
*: Supported with limitations
Open the device's web interface
Open a browser and type the IP address or host name of the Axis device.
If you do not know the IP address, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager to find the device on the network.
Type the username and password. If you access the device for the first time, you must create an administrator account. See Create an administrator account.
For descriptions of all the controls and options in the device’s web interface, see The web interface.
Create an administrator account
The first time you log in to your device, you must create an administrator account.
Enter a username.
Enter a password. See Secure passwords.
Re-enter the password.
Accept the license agreement.
Click Add account.
The device has no default account. If you lose the password for your administrator account, you must reset the device. See Reset to factory default settings.
Secure passwords
Use HTTPS (which is enabled by default) to set your password or other sensitive configurations over the network. HTTPS enables secure and encrypted network connections, thereby protecting sensitive data, such as passwords.
The device password is the primary protection for your data and services. Axis devices do not impose a password policy as they may be used in various types of installations.
To protect your data we strongly recommend that you:
Use a password with at least 8 characters, preferably created by a password generator.
Don’t expose the password.
Change the password at a recurring interval, at least once a year.
Make sure that no one has tampered with the device software
- To make sure that the device has its original AXIS OS, or to take full control of the device after a security attack:
Reset to factory default settings. See Reset to factory default settings.
After the reset, secure boot guarantees the state of the device.
Configure and install the device.
Web interface overview
This video gives you an overview of the device’s web interface.
Configure your device
For how to configure your device, see AXIS Camera Station user manual or third-party solutions.
The web interface
Support for the features and settings described in this section varies between devices. This icon indicates that the feature or setting is only available in some devices.
Show or hide the main menu. Access the release notes. Access the product help. Change the language. Set light theme or dark theme. The user menu contains:
The context menu contains:
|
Status
Device info
Shows information about the device, including AXIS OS version and serial number.
Upgrade AXIS OS: Upgrade the software on your device. Takes you to the Maintenance page where you can do the upgrade. |
Time sync status
Shows NTP synchronization information, including if the device is in sync with an NTP server and the time remaining until the next sync.
NTP settings: View and update the NTP settings. Takes you to the Time and location page where you can change the NTP settings. |
Security
Shows what kind of access to the device that is active, what encryption protocols are in use, and if unsigned apps are allowed. Recommendations to the settings are based on the AXIS OS Hardening Guide.
Hardening guide: Link to AXIS OS Hardening guide where you can learn more about cybersecurity on Axis devices and best practices. |
Connected clients
Shows the number of connections and connected clients.
View details: View and update the list of connected clients. The list shows IP address, protocol, port, state, and PID/process of each connection. |
Device
I/Os and relays
AXIS A9910 Add encryption key: Click to set up an encryption key to ensure encrypted communication. Add AXIS A9910: Click to add an expansion module.
|
I/Os I/O: Turn on to activate connected devices when the port is configured as output.
|
Relays
|
Alarms
Device motion: Turn on to trigger an alarm in your system when it detects a movement of the device. Casing open: Turn on to trigger an alarm in your system when it detects an open door controller case. Turn off this setting for barebone door controllers. External tamper: Turn on to trigger an alarm in your system when it detects an external tamper. For example, when someone opens or closes the external cabinet.
|
Peripherals
Readers
Add reader: Click to add a reader.
Edit: Select a reader and click Edit to make changes for the selected reader. Delete: Select the readers and click Delete to delete the selected readers. |
Wireless locks
You can connect up to 16 ASSA ABLOY Aperio wireless locks using the AH30 Communication Hub. A license is required for the wireless lock.
You must install the AH30 Communication Hub on the secure side.
Connect communication hub: Click to connect the wireless locks. |
Upgrade
Upgrade readers: Click to upgrade the reader’s software. You can only upgrade supported readers when they are online. Upgrade converters: Click to upgrade the converter’s software. You can only upgrade supported converters when they are online. |
Apps
Add app: Install a new app. Find more apps: Find more apps to install. You will be taken to an overview page of Axis apps. Allow unsigned apps: Turn on to allow installation of unsigned apps. View the security updates in AXIS OS and ACAP apps. Note The device’s performance might be affected if you run several apps at the same time. Use the switch next to the app name to start or stop the app. Open: Access the app’s settings. The available settings depend on the application. Some applications don’t have any settings. The context menu can contain one or more of the following options:
|
System
Time and location
Date and time
The time format depends on the web browser’s language settings.
We recommend you synchronize the device’s date and time with an NTP server.
Synchronization: Select an option for the device’s date and time synchronization.
Time zone: Select which time zone to use. Time will automatically adjust to daylight saving time and standard time.
Note The system uses the date and time settings in all recordings, logs, and system settings. |
Device location
Enter where the device is located. Your video management system can use this information to place the device on a map.
|
Network
IPv4
Assign IPv4 automatically: Select IPv4 automatic IP (DHCP) to let the network assign your IP address, subnet mask, and router automatically, without manual configuration. We recommend using automatic IP assignment (DHCP) for most networks. IP address: Enter a unique IP address for the device. Static IP addresses can be assigned at random within isolated networks, provided that each address is unique. To avoid conflicts, we recommend you contact your network administrator before you assign a static IP address. Subnet mask: Enter the subnet mask to define what addresses are inside the local area network. Any address outside the local area network goes through the router. Router: Enter the IP address of the default router (gateway) used to connect devices that are attached to different networks and network segments. Fallback to static IP address if DHCP isn’t available: Select if you want to add a static IP address to use as fallback if DHCP is unavailable and can’t assign an IP address automatically. Note If DHCP isn’t available and the device uses a static address fallback, the static address is configured with a limited scope. |
IPv6
Assign IPv6 automatically: Select to turn on IPv6 and to let the network router assign an IP address to the device automatically. |
Hostname
Assign hostname automatically: Select to let the network router assign a hostname to the device automatically. Hostname: Enter the hostname manually to use as an alternative way of accessing the device. The server report and system log use the hostname. Allowed characters are A–Z, a–z, 0–9 and -. Enable dynamic DNS updates: Allow your device to automatically update its domain name server records whenever its IP address changes. Register DNS name: Enter a unique domain name that points to your device's IP address. Allowed characters are A–Z, a–z, 0–9 and -. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) sets how long a DNS record stays valid before it needs to be updated. |
DNS servers
Assign DNS automatically: Select to let the DHCP server assign search domains and DNS server addresses to the device automatically. We recommend automatic DNS (DHCP) for most networks. Search domains: When you use a hostname that is not fully qualified, click Add search domain and enter a domain in which to search for the hostname the device uses. DNS servers: Click Add DNS server and enter the IP address of the DNS server. This provides the translation of hostnames to IP addresses on your network. |
If DHCP is disabled, features that rely on automatic network configuration, such as hostname, DNS servers, NTP, and others, may stop working.
HTTP and HTTPS
HTTPS is a protocol that provides encryption for page requests from users and for the pages returned by the web server. The encrypted exchange of information is governed by the use of an HTTPS certificate, which guarantees the authenticity of the server.
To use HTTPS on the device, you must install an HTTPS certificate. Go to System > Security to create and install certificates.
Allow access through: Select if a user is allowed to connect to the device through the HTTP, HTTPS, or both HTTP and HTTPS protocols. Note If you view encrypted web pages through HTTPS, you might experience a drop in performance, especially when you request a page for the first time. HTTP port: Enter the HTTP port to use. The device allows port 80 or any port in the range 1024-65535. If you are logged in as an administrator, you can also enter any port in the range 1-1023. If you use a port in this range, you get a warning. HTTPS port: Enter the HTTPS port to use. The device allows port 443 or any port in the range 1024-65535. If you are logged in as an administrator, you can also enter any port in the range 1-1023. If you use a port in this range, you get a warning. Certificate: Select a certificate to enable HTTPS for the device. |
Network discovery protocols
Bonjour®: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. Bonjour name: Enter a friendly name to be visible on the network. The default name is the device name and MAC address. UPnP®: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. UPnP name: Enter a friendly name to be visible on the network. The default name is the device name and MAC address. WS-Discovery: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. LLDP and CDP: Turn on to allow automatic discovery on the network. Turning LLDP and CDP off can impact the PoE power negotiation. To resolve any issues with the PoE power negotiation, configure the PoE switch for hardware PoE power negotiation only. |
One-click cloud connection
One-click cloud connection (O3C) together with an O3C service provides easy and secure internet access to live and recorded video from any location. For more information, see axis.com/end-to-end-solutions/hosted-services.
Allow O3C:
Proxy settings: If needed, enter the proxy settings to connect to the proxy server. Host: Enter the proxy server’s address. Port: Enter the port number used for access. Login and Password: If needed, enter username and password for the proxy server. Authentication method:
Owner authentication key (OAK): Click Get key to fetch the owner authentication key. This is only possible if the device is connected to the internet without a firewall or proxy. |
SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) allows remote management of network devices.
SNMP: Select the version of SNMP to use.
Note All Axis Video MIB traps are enabled when you turn on SNMP v1 and v2c traps. For more information, see AXIS OS Portal > SNMP.
|
Security
Certificates
Certificates are used to authenticate devices on a network. The device supports two types of certificates:
These formats are supported:
Important If you reset the device to factory default, all certificates are deleted. Any pre-installed CA certificates are reinstalled. Add certificate : Click to add a certificate. A step-by-step guide opens up.
The context menu contains:
Secure keystore:
|
Network access control and encryption
IEEE 802.1x IEEE 802.1x is an IEEE standard for port-based network admission control providing secure authentication of wired and wireless network devices. IEEE 802.1x is based on EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol). To access a network protected by IEEE 802.1x, network devices must authenticate themselves. The authentication is performed by an authentication server, typically a RADIUS server (for example, FreeRADIUS and Microsoft Internet Authentication Server). IEEE 802.1AE MACsec IEEE 802.1AE MACsec is an IEEE standard for media access control (MAC) security that defines connectionless data confidentiality and integrity for media access independent protocols. Certificates When configured without a CA certificate, server certificate validation is disabled and the device tries to authenticate itself regardless of what network it is connected to. When using a certificate, in Axis' implementation, the device and the authentication server authenticate themselves with digital certificates using EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security). To allow the device to access a network protected through certificates, you must install a signed client certificate on the device. Authentication method: Select an EAP type used for authentication. Client certificate: Select a client certificate to use IEEE 802.1x. The authentication server uses the certificate to validate the client’s identity. CA certificates: Select CA certificates to validate the authentication server’s identity. When no certificate is selected, the device tries to authenticate itself regardless of what network it is connected to. EAP identity: Enter the user identity associated with the client certificate. EAPOL version: Select the EAPOL version that is used in the network switch. Use IEEE 802.1x: Select to use the IEEE 802.1x protocol. These settings are only available if you use IEEE 802.1x PEAP-MSCHAPv2 as the authentication method:
These settings are only available if you use IEEE 802.1ae MACsec (Static CAK/Pre-Shared Key) as the authentication method:
|
Prevent brute-force attacks
Blocking: Turn on to block brute-force attacks. A brute-force attack uses trial-and-error to guess login info or encryption keys. Blocking period: Enter the number of seconds to block a brute-force attack. Blocking conditions: Enter the number of authentication failures allowed per second before the block starts. You can set the number of failures allowed both on page level and device level. |
Firewall
Firewall: Turn on to activate the firewall.
To make exceptions to the default policy, you can create rules that allows or blocks connections to the device from specific addresses, protocols, and ports. + New rule: Click to create a rule.
LIMIT: Select to accept connections from devices that match the criteria defined in the rule but apply limits to reduce excessive traffic.
Test rules: Click to test the rules that you have defined.
|
Custom signed AXIS OS certificate
To install test software or other custom software from Axis on the device, you need a custom signed AXIS OS certificate. The certificate verifies that the software is approved by both the device owner and Axis. The software can only run on a specific device which is identified by its unique serial number and chip ID. Only Axis can create custom signed AXIS OS certificates, since Axis holds the key to sign them. Install: Click to install the certificate. You need to install the certificate before you install the software. The context menu contains:
|
Accounts
Accounts
Add account: Click to add a new account. You can add up to 100 accounts. Account: Enter a unique account name. New password: Enter a password for the account. Passwords must be 1 to 64 characters long. Only ASCII printable characters (code 32 to 126) are allowed in the password, for example, letters, numbers, punctuation, and some symbols. Repeat password: Enter the same password again. Privileges:
The context menu contains: Update account: Edit the account properties. Delete account: Delete the account. You can’t delete the root account. |
SSH accounts
Add SSH account: Click to add a new SSH account.
Account: Enter a unique account name. New password: Enter a password for the account. Passwords must be 1 to 64 characters long. Only ASCII printable characters (code 32 to 126) are allowed in the password, for example, letters, numbers, punctuation, and some symbols. Repeat password: Enter the same password again. Comment: Enter a comment (optional). The context menu contains: Update SSH account: Edit the account properties. Delete SSH account: Delete the account. You can’t delete the root account. |
Virtual host
Add virtual host: Click to add a new virtual host. Enabled: Select to use this virtual host. Server name: Enter the name of the server. Only use numbers 0-9, letters A-Z, and hyphen (-). Port: Enter the port the server is connected to. Type: Select the type of authentication to use. Select between Basic, Digest, Open ID, and Client Credential Grant. HTTPS: Select to use HTTPS. The context menu contains:
|
OpenID Configuration
If you can't use OpenID to sign in, use the Digest or Basic credentials you used when you configured OpenID to sign in.
Client ID: Enter the OpenID username. Outgoing Proxy: Enter the proxy address for the OpenID connection to use a proxy server. Admin claim: Enter a value for the admin role. Provider URL: Enter the web link for the API endpoint authentication. Format should be https://[insert URL]/.well-known/openid-configuration Operator claim: Enter a value for the operator role. Require claim: Enter the data that should be in the token. Viewer claim: Enter the value for the viewer role. Remote user: Enter a value to identify remote users. This assists to display the current user in the device’s web interface. Scopes: Optional scopes that could be part of the token. Client secret: Enter the OpenID password Save: Click to save the OpenID values. Enable OpenID: Turn on to close current connection and allow device authentication from the provider URL. |
MQTT
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a standard messaging protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT). It was designed for simplified IoT integration and is used in a wide variety of industries to connect remote devices with a small code footprint and minimal network bandwidth. The MQTT client in Axis device software can simplify integration of data and events produced in the device to systems which are not video management software (VMS). Set up the device as an MQTT client. MQTT communication is based on two entities, the clients and the broker. The clients can send and receive messages. The broker is responsible for routing messages between clients. You can learn more about MQTT in AXIS OS Knowledge base. |
ALPN
ALPN is a TLS/SSL extension that allows for the selection of an application protocol during the handshake phase of the connection between the client and server. This is used to enable MQTT traffic over the same port that is used for other protocols, such as HTTP. In some cases, there might not be a dedicated port open for MQTT communication. A solution in such cases is to use ALPN to negotiate the use of MQTT as the application protocol on a standard port, allowed by the firewalls. |
MQTT client
Connect: Turn on or off the MQTT client. Status: Shows the current status of the MQTT client. Broker Host: Enter the hostname or IP address of the MQTT server. Protocol: Select which protocol to use. Port: Enter the port number.
ALPN protocol: Enter the ALPN protocol name provided by your MQTT broker provider. This is only applicable with MQTT over SSL and MQTT over WebSocket Secure. Username: Enter the username that the client will use to access the server. Password: Enter a password for the username. Client ID: Enter a client ID. The client identifier is sent to the server when the client connects to it. Clean session: Controls the behavior at connection and disconnection time. When selected, the state information is discarded at connect and disconnect. HTTP proxy: A URL with a maximum length of 255 bytes. You can leave the field empty if you don't want to use an HTTP proxy. HTTPS proxy: A URL with a maximum length of 255 bytes. You can leave the field empty if you don't want to use an HTTPS proxy. Keep alive interval: Enables the client to detect when the server is no longer available without having to wait for the long TCP/IP timeout. Timeout: The time interval in seconds to allow a connect to complete. Default value: 60 Device topic prefix: Used in the default values for the topic in the connect message and LWT message on the MQTT client tab, and in the publication conditions on the MQTT publication tab. Reconnect automatically: Specifies whether the client should reconnect automatically after a disconnect. Connect message Specifies if a message should be sent out when a connection is established. Send message: Turn on to send messages. Use default: Turn off to enter your own default message. Topic: Enter the topic for the default message. Payload: Enter the content for the default message. Retain: Select to keep the state of client on this Topic QoS: Change the QoS layer for the packet flow. Last Will and Testament message The Last Will Testament (LWT) lets a client provide a testament along with its credentials when connecting to the broker. If the client disconnects ungracefully at some point later (maybe because his power source died), it can let the broker deliver a message to other clients. This LWT message has the same form as an ordinary message and gets routed via the same mechanics. Send message: Turn on to send messages. Use default: Turn off to enter your own default message. Topic: Enter the topic for the default message. Payload: Enter the content for the default message. Retain: Select to keep the state of client on this Topic QoS: Change the QoS layer for the packet flow. |
MQTT publication
Use default topic prefix: Select to use the default topic prefix, that is defined in the device topic prefix in the MQTT client tab. Include condition: Select to include the topic that describes the condition in the MQTT topic. Include namespaces: Select to include ONVIF topic namespaces in the MQTT topic. Include serial number: Select to include the device’s serial number in the MQTT payload. Add condition: Click to add a condition. Retain: Defines which MQTT messages are sent as retained.
QoS: Select the desired level for the MQTT publication. |
MQTT subscriptions
Add subscription: Click to add a new MQTT subscription. Subscription filter: Enter the MQTT topic that you want to subscribe to. Use device topic prefix: Add the subscription filter as prefix to the MQTT topic. Subscription type:
QoS: Select the desired level for the MQTT subscription. |
Accessories
I/O ports
Use digital input to connect external devices that can toggle between an open and closed circuit, for example, PIR sensors, door or window contacts, and glass break detectors.
Use digital output to connect external devices such as relays and LEDs. You can activate connected devices through the VAPIX® Application Programming Interface or the web interface.
Port Name: Edit the text to rename the port. Direction: indicates that the port is an input port. indicates that it’s an output port. If the port is configurable, you can click the icons to change between input and output. Normal state: Click for open circuit, and for closed circuit. Current state: Shows the current state of the port. The input or output is activated when the current state is different from the normal state. An input on the device has an open circuit when it’s disconnected or when there is a voltage above 1 VDC. Note During restart, the output circuit is open. When the restart is complete, the circuit goes back to the normal position. If you change any settings on this page, the output circuits go back to their normal positions regardless of any active triggers. Supervised: Turn on to make it possible to detect and trigger actions if someone tampers with the connection to digital I/O devices. In addition to detecting if an input is open or closed, you can also detect if someone has tampered with it (that is, cut or shorted). To supervise the connection requires additional hardware (end-of-line resistors) in the external I/O loop. |
Logs
Reports and logs
Reports
Logs
|
Network trace
Important A network trace file might contain sensitive information, for example certificates or passwords. A network trace file can help you troubleshoot problems by recording activity on the network. Trace time: Select the duration of the trace in seconds or minutes, and click Download. |
Remote system log
Syslog is a standard for message logging. It allows separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, which indicates the software type generating the message, and assigned a severity level.
Server: Click to add a new server. Host: Enter the hostname or IP address of the server. Format: Select which syslog message format to use.
Protocol: Select the protocol to use:
Port: Edit the port number to use a different port. Severity: Select which messages to send when triggered. Type: Select the type of logs you want to send. Test server setup: Send a test message to all servers before you save the settings. CA certificate set: See the current settings or add a certificate. |
Maintenance
Restart: Restart the device. This does not affect any of the current settings. Running applications restart automatically. Restore: Return most settings to the factory default values. Afterwards you must reconfigure the device and apps, reinstall any apps that didn’t come preinstalled, and recreate any events and presets. Important The only settings saved after restore are:
Factory default: Return all settings to the factory default values. Afterwards you must reset the IP address to make the device accessible. Note All Axis device software is digitally signed to ensure that you only install verified software on your device. This further increases the overall minimum cybersecurity level of Axis devices. For more information, see the white paper “Axis Edge Vault” at axis.com. AXIS OS upgrade: Upgrade to a new AXIS OS version. New releases can contain improved functionality, bug fixes, and completely new features. We recommend you to always use the latest AXIS OS release. To download the latest release, go to axis.com/support.
AXIS OS rollback: Revert to the previously installed AXIS OS version. |
Learn more
Cybersecurity
For product-specific information about cybersecurity, see the product's datasheet at axis.com.
For in-depth information about cybersecurity in AXIS OS, read the AXIS OS Hardening guide.
Signed OS
Signed OS is implemented by the software vendor signing the AXIS OS image with a private key. When the signature is attached to the operating system, the device will validate the software before installing it. If the device detects that the integrity of the software is compromised, the AXIS OS upgrade will be rejected.
Secure boot
Secure boot is a boot process that consists of an unbroken chain of cryptographically validated software, starting in immutable memory (boot ROM). Being based on the use of signed OS, secure boot ensures that a device can boot only with authorized software.
Axis Edge Vault
Axis Edge Vault provides a hardware-based cybersecurity platform that safeguards the Axis device. It offers features to guarantee the device’s identity and integrity and to protect your sensitive information from unauthorized access. It builds on a strong foundation of cryptographic computing modules (secure element and TPM) and SoC security (TEE and secure boot), combined with expertise in edge device security.
Axis device ID
Being able to verify the origin of the device is key to establishing trust in the device identity. During production, devices with Axis Edge Vault are assigned a unique, factory-provisioned, and IEEE 802.1AR-compliant Axis device ID certificate. This works like a passport to prove the origin of the device. The device ID is securely and permanently stored in the secure keystore as a certificate signed by Axis root certificate. The device ID can be leveraged by the customer’s IT infrastructure for automated secure device onboarding and secure device identification
To learn more about the cybersecurity features in Axis devices, go to axis.com/learning/white-papers and search for cybersecurity.
Specifications
Product overview
- Network connector
- Grounding position
- Relay jumper
- Power connector
- Relay connector
- Door connector
- Reader connector
- Auxiliary connector
- External connectors
- Control button
LED indicators
| LED | Color | Indication |
| Status | Green | Steady green for normal operation. |
| Amber | Steady during startup and when restoring settings. | |
| Red | Slow flash for failed upgrade. | |
| Network | Green | Steady for connection to a 100 MBit/s network. Flashes for network activity. |
| Amber | Steady for connection to a 10 MBit/s network. Flashes for network activity. | |
| Unlit | No network connection. | |
| Power | Green | Normal operation. |
| Amber | Flashes green/amber during firmware upgrade. | |
| Relay | Green | Relay active.(1) |
| Unlit | Relay inactive. |
- Relay is active when COM is connected to NO.
Buttons
Control button
- The control button is used for:
Resetting the product to factory default settings. See Reset to factory default settings.
Connectors
Network connector
RJ45 Ethernet connector with Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+).
UL: Power over Ethernet (PoE) shall be over Ethernet IEEE 802.3af/802.3at Type 1 Class 3 or Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+) IEEE 802.3at Type 2 Class 4 power limited injector that provides 44–57 V DC, 15.4 W / 30 W. Power over Ethernet (PoE) has been evaluated by UL with AXIS T8133 Midspan 30 W 1-port.
Power priority
This device can be powered by either PoE or DC input. See Network connector and Power connector.
When PoE and DC are both connected before the device is powered, PoE is used for powering.
PoE and DC are both connected and PoE is currently powering. When PoE is lost, the device uses DC for powering without restart.
PoE and DC are both connected and DC is currently powering. When DC is lost, the device restarts and uses PoE for powering.
When DC is used during startup and PoE is connected after the device has started, DC is used for powering.
When PoE is used during startup and DC is connected after the device has started, PoE is used for powering.
Reader connector
One 8-pin terminal block supporting both OSDP and Wiegand protocols for communication with the reader.
It can connect up to two OSDP readers (multi-drop) or one Wiegand reader. 500 mA at 12 V DC is reserved for all readers connected to the door controller.
Configured for one OSDP reader
| Function | Pin | Note | Specifications |
| DC ground (GND) | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| DC output (+12 V) | 2 | Supplies power to reader. | 12 V DC, max 500 mA |
| A | 3 | Half duplex | |
| B | 4 | Half duplex |
Configured for two OSDP readers (multi-drop)
| Function | Pin | Note | Specifications |
| DC ground (GND) | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| DC output (+12 V) | 2 | Supplies power to both readers. | 12 V DC, max 500 mA combined for both readers |
| A | 3 | Half duplex | |
| B | 4 | Half duplex |
- When the reader is powered by the controller, the qualified cable length is up to 200 m (656 ft). Verified only for Axis readers.
- When the reader is not powered by the controller, the qualified cable length for reader data is up to 1000 m (3280,8 ft) if the following cable requirements are met: 1 twisted pair with shield, AWG 24, 120 ohm impedance. Verified only for Axis readers.
Configured for one Wiegand reader
| Function | Pin | Note | Specifications |
| DC ground (GND) | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| DC output (+12 V) | 2 | Supplies power to reader. | 12 V DC, max 500 mA |
| D0 | 3 | ||
| D1 | 4 | ||
| LED 1 | 5 | Red LED | |
| LED 2 | 6 | Green LED | |
| TAMPER | 7 | Digital input — Connect to pin 1 to activate, or leave floating (unconnected) to deactivate. | 0 to max 30 V DC |
| BUZZER | 8 | Digital output — If used with an inductive load, e.g., a relay, connect a diode in parallel with the load, to protect against voltage transients. | 0 to max 30 V DC, open drain, 100 mA |
- When the reader is powered by the controller, the qualified cable length is up to 150 m (500 ft).
- When the reader is not powered by the controller, the qualified cable length for reader data is up to 150 m (500 ft) if the following cable requirement is met: AWG 22.
Door connector
One 4-pin terminal block for door monitoring devices (digital input).
Door monitor supports supervision with end of line resistors. If the connection is interrupted, an alarm is triggered. To use supervised inputs, install end of line resistors. Use the connection diagram for supervised inputs. See Supervised inputs.
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground | 1, 3 | 0 V DC | |
| Input | 2, 4 | For communicating with door monitor. Digital input or Supervised input — Connect to pin 1 or 3 respectively to activate, or leave floating (unconnected) to deactivate. | 0 to max 30 V DC |
The qualified cable length is up to 200 m (656 ft) if the following cable requirement is met: AWG 24.
Relay connector
One 4-pin terminal block for form C relays that can be used, for example, to control a lock or an interface to a gate.
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground (GND) | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| NO | 2 | Normally open. For connecting relay devices. Connect a fail-secure lock between NO and DC ground. The two relay pins are galvanically separated from the rest of the circuitry if the jumpers are not used. | Max current = 2 A Max voltage = 30 V DC |
| COM | 3 | Common | |
| NC | 4 | Normally closed. For connecting relay devices. Connect a fail-safe lock between NC and DC ground. The two relay pins are galvanically separated from the rest of the circuitry if the jumpers are not used. |
Relay power jumper
When the relay power jumper is fitted, it connects 12 V DC or 24 V DC to the relay COM pin.
It can be used to connect a lock between the GND and NO, or GND and NC pins.
| Power source | Max power at 12 V DC | Max power at 24 V DC |
| DC IN | 1 600 mA | 800 mA |
| PoE | 900 mA | 450 mA |
If the lock is non-polarized, we recommend you to add an external flyback diode.
Auxiliary connector
Use the auxiliary connector with external devices in combination with, for example, motion detection, event triggering, and alarm notifications. In addition to the 0 V DC reference point and power (DC output), the auxiliary connector provides the interface to:
- Digital input
- For connecting devices that can toggle between an open and closed circuit, for example PIR sensors, door/window contacts, and glass break detectors.
- Supervised input
- Enables possibility to detect tampering on a digital input.
- Digital output
- For connecting external devices such as relays and LEDs. Connected devices can be activated by the VAPIX® Application Programming Interface or from the product’s webpage.
4-pin terminal block
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| DC output | 2 | Can be used to power auxiliary equipment. Note: This pin can only be used as power out. | 12 V DC Max load = 50 mA in total |
| Configurable (Input or Output) | 3–4 | Digital input or supervised input – Connect to pin 1 to activate, or leave floating (unconnected) to deactivate. To use supervised input, install end-of-line resistors. See connection diagram for information about how to connect the resistors. | 0 to max 30 V DC |
| Digital output – Internally connected to pin 1 (DC ground) when active, and floating (unconnected) when inactive. If used with an inductive load, e.g., a relay, connect a diode in parallel with the load, to protect against voltage transients. I/Os are capable of driving 12 V DC, 50 mA (combined max) external load, if internal 12 V DC output (pin 2) is used. In the case of using open drain connections in combination with an external power supply, then the I/Os can manage DC supply of 0–30 V DC, 100 mA each. | 0 to max 30 V DC, open drain, 100 mA |
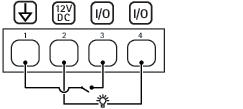
- DC ground
- DC output 12 V
- I/O configured as input
- I/O configured as output
External connector
Two 2-pin terminal blocks for external devices, for example glass break or fire detectors.
UL: The connector has not been evaluated by UL for burglar or fire alarm use.
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| TAMPER | 2 | Digital input – Connect to pin 1 to activate, or leave floating (unconnected) to deactivate. | 0 to max 30 V DC |
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| ALARM | 2 | Digital input – Connect to pin 1 to activate, or leave floating (unconnected) to deactivate. | 0 to max 30 V DC |
Power connector
2-pin terminal block for DC power input. Use a Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) compliant limited power source (LPS) with either a rated output power limited to ≤100 W or a rated output current limited to ≤5 A.
| Function | Pin | Notes | Specifications |
| DC ground (GND) | 1 | 0 V DC | |
| DC input | 2 | For powering the device when not using Power over Ethernet. Note: This pin can only be used as power in. | 12 V DC, max 36 W |
UL: DC power to be supplied by a UL 603 listed power supply, depending on application, with appropriate ratings.
Supervised inputs
To use supervised inputs, install end of line resistors according to the diagram below.
Parallel first connection
The resistor values must be 4.7 kΩ and 22 kΩ.
Serial first connection
The resistor values must be the same and possible values are 1 kΩ, 2.2 kΩ, 4.7 kΩ and 10 kΩ.
It is recommended to use twisted and shielded cables. Connect shielding to 0 V DC.
Troubleshooting
Reset to factory default settings
Reset to factory default should be used with caution. A reset to factory default resets all settings, including the IP address, to the factory default values.
To reset the product to the factory default settings:
Disconnect power from the product.
Press and hold the control button while reconnecting power. See Product overview.
Keep the control button pressed for 25 seconds until the status LED indicator turns amber for the second time.
Release the control button. The process is complete when the status LED indicator turns green. If no DHCP server is available on the network, the device IP address will default to one of the following:
Devices with AXIS OS 12.0 and later: Obtained from the link-local address subnet (169.254.0.0/16)
Devices with AXIS OS 11.11 and earlier: 192.168.0.90/24
Use the installation and management software tools, assign an IP address, set the password, and access the product.
You can also reset parameters to factory default through the device’s web interface. Go to Maintenance > Factory default and click Default.
AXIS OS options
Axis offers device software management according to either the active track or the long-term support (LTS) tracks. Being on the active track means continuously getting access to all the latest product features, while the LTS tracks provide a fixed platform with periodic releases focused mainly on bug fixes and security updates.
Using AXIS OS from the active track is recommended if you want to access the newest features, or if you use Axis end-to-end system offerings. The LTS tracks are recommended if you use third-party integrations, which are not continuously validated against the latest active track. With LTS, the products can maintain cybersecurity without introducing any significant functional changes or affecting any existing integrations. For more detailed information about Axis device software strategy, go to axis.com/support/device-software.
Check the current AXIS OS version
AXIS OS determines the functionality of our devices. When you troubleshoot a problem, we recommend that you to start by checking the current AXIS OS version. The latest version might contain a correction that fixes your particular problem.
To check the current AXIS OS version:
Go to the device’s web interface > Status.
Under Device info, see the AXIS OS version.
Upgrade AXIS OS
- When you upgrade the device software, your preconfigured and customized settings are saved. Axis Communications AB can't guarantee that the settings are saved, even if the features are available in the new AXIS OS version.
- Starting from AXIS OS 12.6, you must install every LTS version between your device’s current version and the target version. For example, if the currently installed device software version is AXIS OS 11.2, you have to install the LTS version AXIS OS 11.11 before you can upgrade the device to AXIS OS 12.6. For more information, see AXIS OS Portal: Upgrade path.
- Make sure the device remains connected to the power source throughout the upgrade process.
- When you upgrade the device with the latest AXIS OS version in the active track, the product receives the latest functionality available. Always read the upgrade instructions and release notes available with each new release before you upgrade. To find the latest AXIS OS version and the release notes, go to axis.com/support/device-software.
- Because the database of users, groups, credentials, and other data are updated after a AXIS OS upgrade, the first start-up could take a few minutes to complete. The time required is dependent on the amount of data.
Download the AXIS OS file to your computer, available free of charge at axis.com/support/device-software.
Log in to the device as an administrator.
Go to Maintenance > AXIS OS upgrade and click Upgrade.
- When the upgrade has finished, the product restarts automatically.
When the product has been restarted, clear the web browser's cache.
Technical problems and possible solutions
Problems upgrading AXIS OS
AXIS OS upgrade failed If the upgrade fails, the device reloads the previous version. The most common reason is that the wrong AXIS OS file has been uploaded. Check that the name of the AXIS OS file corresponds to your device and try again. |
Problems after AXIS OS upgrade If you experience problems after the upgrade, roll back to the previously installed version from the Maintenance page. |
Problems setting the IP address
Can’t set the IP address
|
Problems accessing the device
Can’t log in when accessing the device from a browser When HTTPS is enabled, make sure that you use the correct protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) when you try to log in. You might need to manually type If you’ve lost the password for the root account, you must reset the device to the factory default settings. For instructions, see Reset to factory default settings. |
The IP address has been changed by DHCP IP addresses obtained from a DHCP server are dynamic and could change. If the IP address has been changed, use AXIS IP Utility or AXIS Device Manager to locate the device on the network. Identify the device using its model or serial number, or by the DNS name (if the name has been configured). If required, you can assign a static IP address manually. For instructions, go to axis.com/support. |
Certificate error when using IEEE 802.1X For authentication to work properly, the date and time settings in the Axis device must be synchronized with an NTP server. Go to System > Date and time. |
The browser isn’t supported For a list of recommended browsers, see Browser support. |
Can’t access the device externally To access the device externally, we recommend you to use one of the following applications for Windows®:
For instructions and download, go to axis.com/vms. |
Problems with MQTT
Can’t connect over port 8883 with MQTT over SSL The firewall blocks traffic that uses port 8883 since it’s regarded insecure. In some cases the server/broker might not provide a specific port for MQTT communication. It might still be possible to use MQTT over a port normally used for HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
|
Problems with operating the device
Front heater and wiper aren’t working If the front heater or wiper are not turning on, confirm that the top cover is properly fastened to the bottom of the housing unit. |
If you can’t find what you’re looking for here, try the troubleshooting section at axis.com/support.
Contact support
If you need more help, go to axis.com/support.